1. Workstation¶
Flopsar Workstation is a GUI client of the Flopsar environment.
1.1. Installation¶
Installation is straightforward, just copy the workstation.zip file to your machine and uncompress it. Next, execute the following command to start the application:
$ java -jar flopsar-workstation-VER-jfx.jar
Note
You should have your Java environment set before you try to run the workstation application.
1.2. Accessing Flopsar Environment¶
When you execute the above command a logon window Fig. 1.1 should appear.

Fig. 1.1 Workstation Logon: Remote Access
If you want to connect to some remote manager, select the Remote radio button. If you want to access your local copy of some database, select the Local radio button.
1.2.1. Remote Access¶
If you run workstation for the first time, the Connection ID combo box control is empty. In order to connect to your manager instance, you must specify some connection identifier (label) and input manager socket address in the form host:port. You must also provide your credentials and then click the Connect button. When you log to the manager instance successfully, the logon window disappears and the main application window Fig. 1.3 appears instead. After a successful connection, your connection data are stored locally so that next time you start the application, the combo box will be filled with this stored connection information.
Important
Default credentials when using Flopsar Internal Authentication are as follows: the username is admin and the password is flopsar.
1.2.2. Local Access¶
In order to access your database locally, you just need to get the archive file from a selected database instance and copy it to your local disk. Next, select the Local radio button in the logon window Fig. 1.1 and then select the Archive file radio button. Click on the Open… button and select your archive file. When you press the Connect button, the archive will be decompressed and a new workstation window Fig. 1.4 will appear.

Fig. 1.2 Workstation Logon: Local Access
Next time you access the local storage, select Storage radio button and point to the uncompressed storage directory.
1.3. Start Page¶
After you logged to the application remotely, you should see its start page Fig. 1.3. You can see there six tiles, which take you to different areas of the application. At the bottom, there is your current connection information to your manager, your current time zone and the number of connected databases. On the right side, there is a memory usage information of the application.
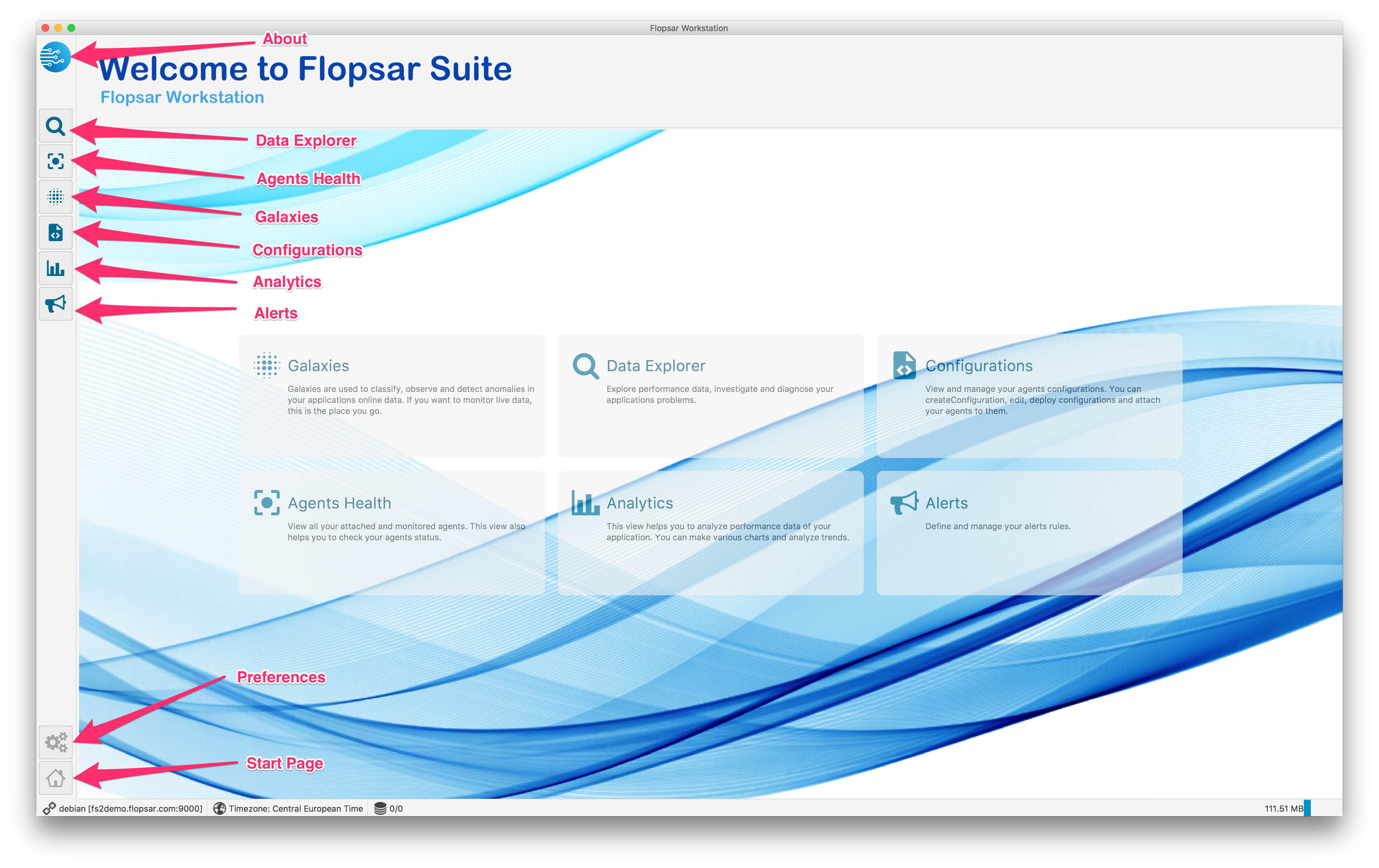
Fig. 1.3 Workstation: Remote Start Page
If you access your local storage, you do not see the same workstation functionalities as in the remote access. That is because you do not connect to any manager instance, and the workstation runs in a viewer mode. At the bottom, there is the current local storage identifier, your current time zone and the number of connected databases (only one in this case).
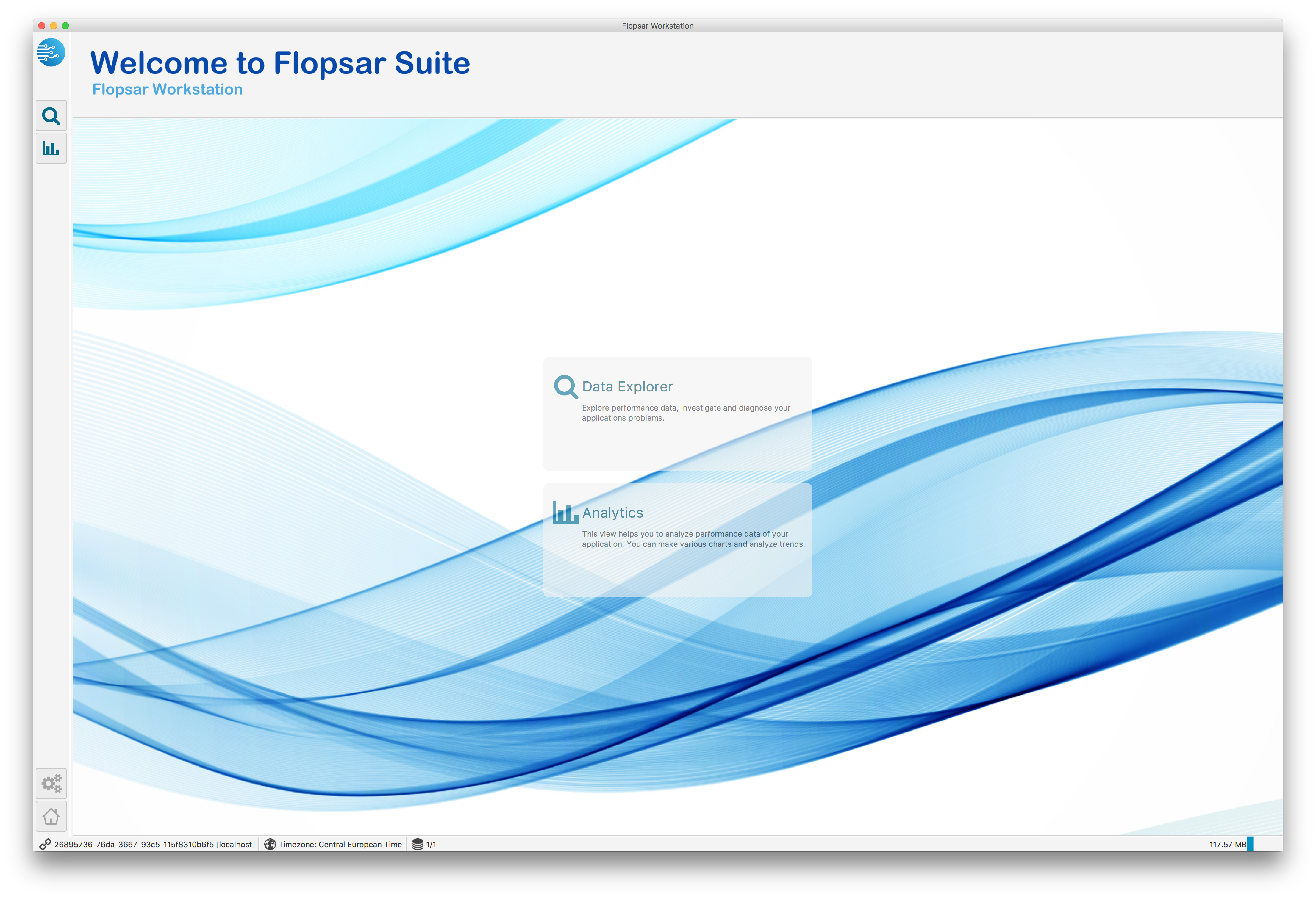
Fig. 1.4 Workstation: Local Start Page
In both cases (remote and local), if you click the database icon, a popup window Fig. 1.5 with a list will appear. This list contains addresses of databases your manager is aware of. There is a link icon, at the beginning of each entry, which denotes a connection status. If the link is green, then the corresponding database connection is established. The link turns red if the connection is lost or does not exist.
Note
In case of local access, the database address is always localhost.
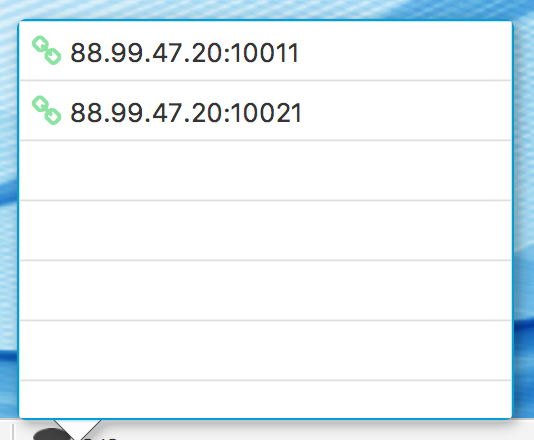
Fig. 1.5 Connected Databases
The start pages contain a few tiles with captions and descriptions. By clicking you are accessing different functionalities of the application: the Galaxies tile will take you to a view where you can manage your galaxies (see Galaxies for details). The Configurations tile will take you to a view where you can manage your configurations (see Managing Agent Configurations for details). The Agents Health leads to a view where you can observe all the available agents (see Monitoring Agents Health for details). The Alerts tile leads to a view where you can manage your alert rules (see Managing Alerts for details), the Analytics tile leads to a view where you can manage and analyze your selected metrics (see Analytics for details). The Data Explorer tile leads to a view, where you can query the databases for instrumentation and environment data.
1.4. Configuration¶
workstation stores its settings locally, on the machine it runs on. It makes use of Java Preferences API to store its configuration. The physical location of the settings depends on a platform the workstation runs.
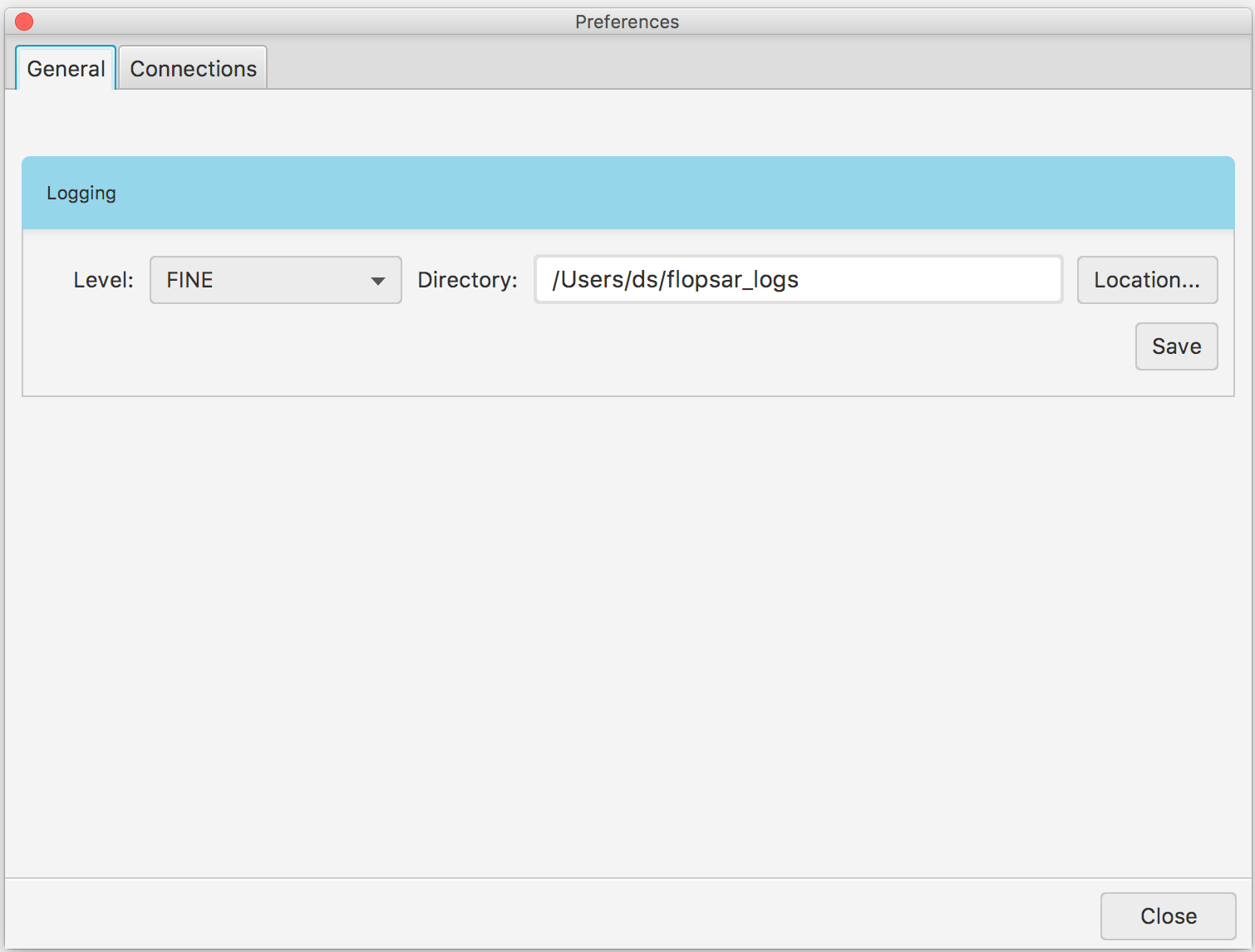
When you exit the application, it stores its current settings. These settings include the main application window size, some tables columns width, galaxy colors and the like. Besides the layout settings, your manager connections information is also stored in these settings. You can either edit or delete these connections in the preferences window Fig. 1.6.
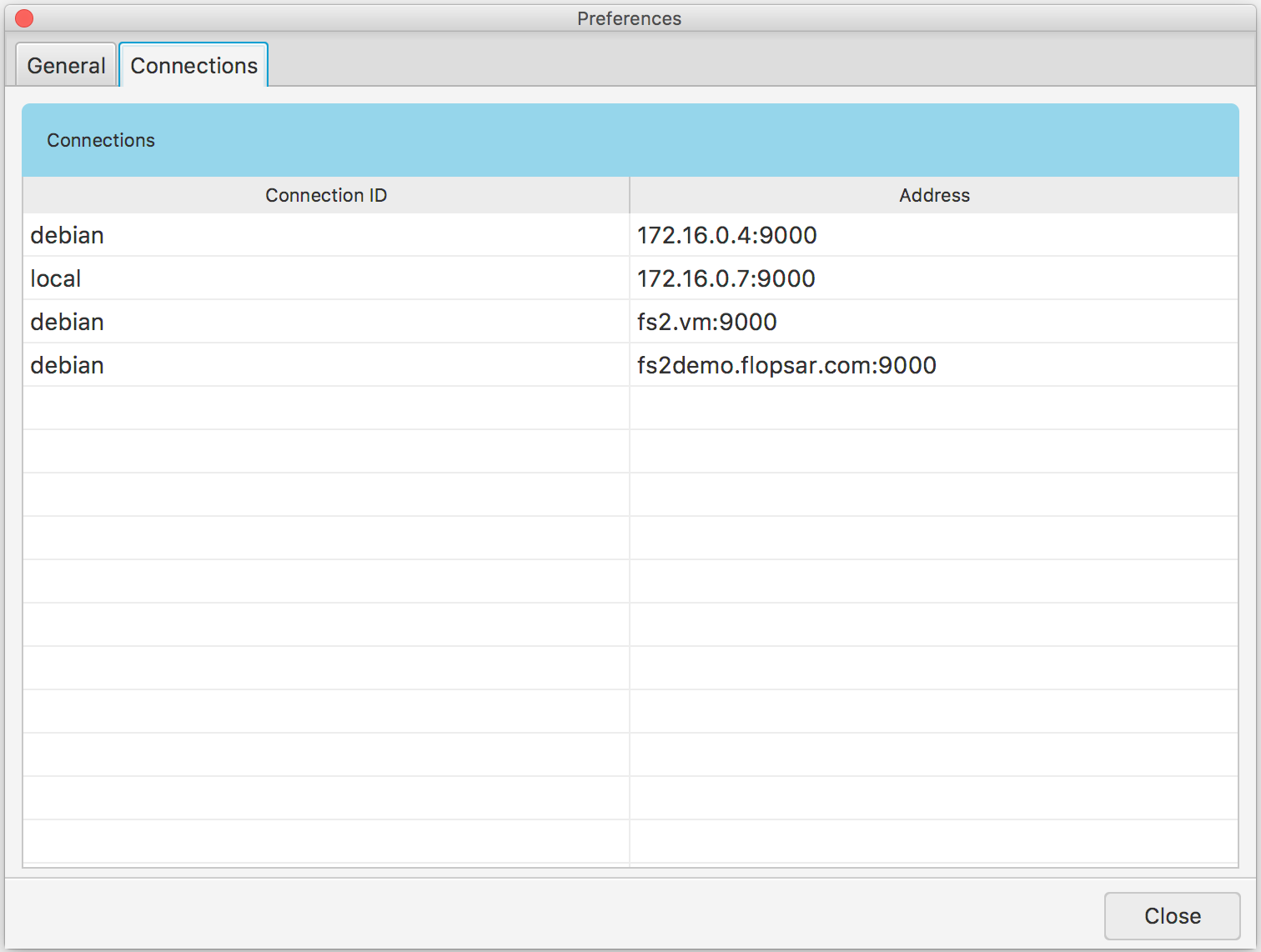
Fig. 1.6 Preferences: Connections
1.5. Managing Agent Configurations¶
Agents configurations are managed from workstation. You must click the configuration tile in Fig. 1.3 view to get the list of all the configurations.
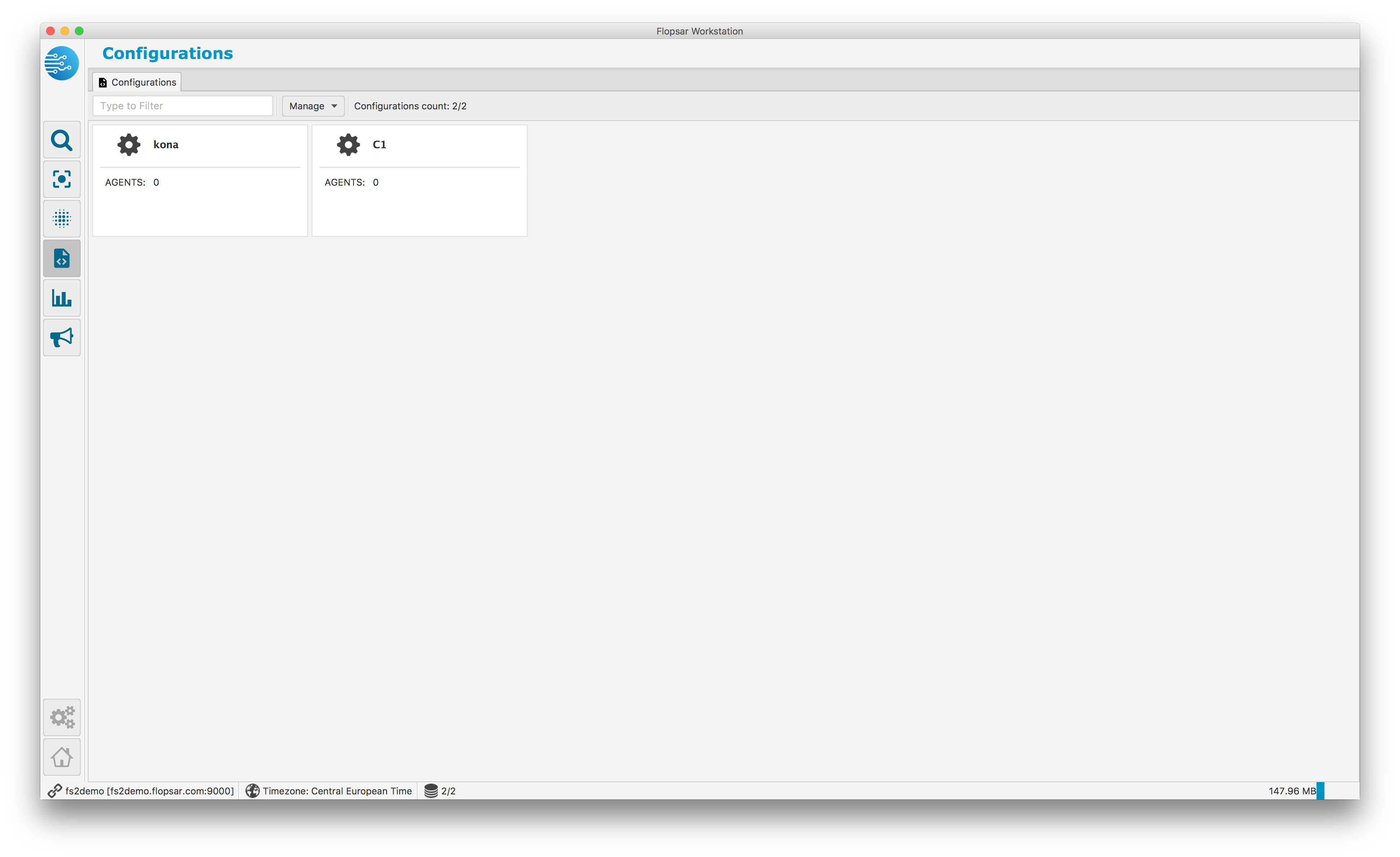
Fig. 1.8 Agents’ Configurations
In order to add a new configuration, click the Manage –> Add New… menu item. A popup window will appear where you must specify a label for the configuration. When you click the Save button, a new tile will appear in the configurations set. Click the tile to edit the configuration.
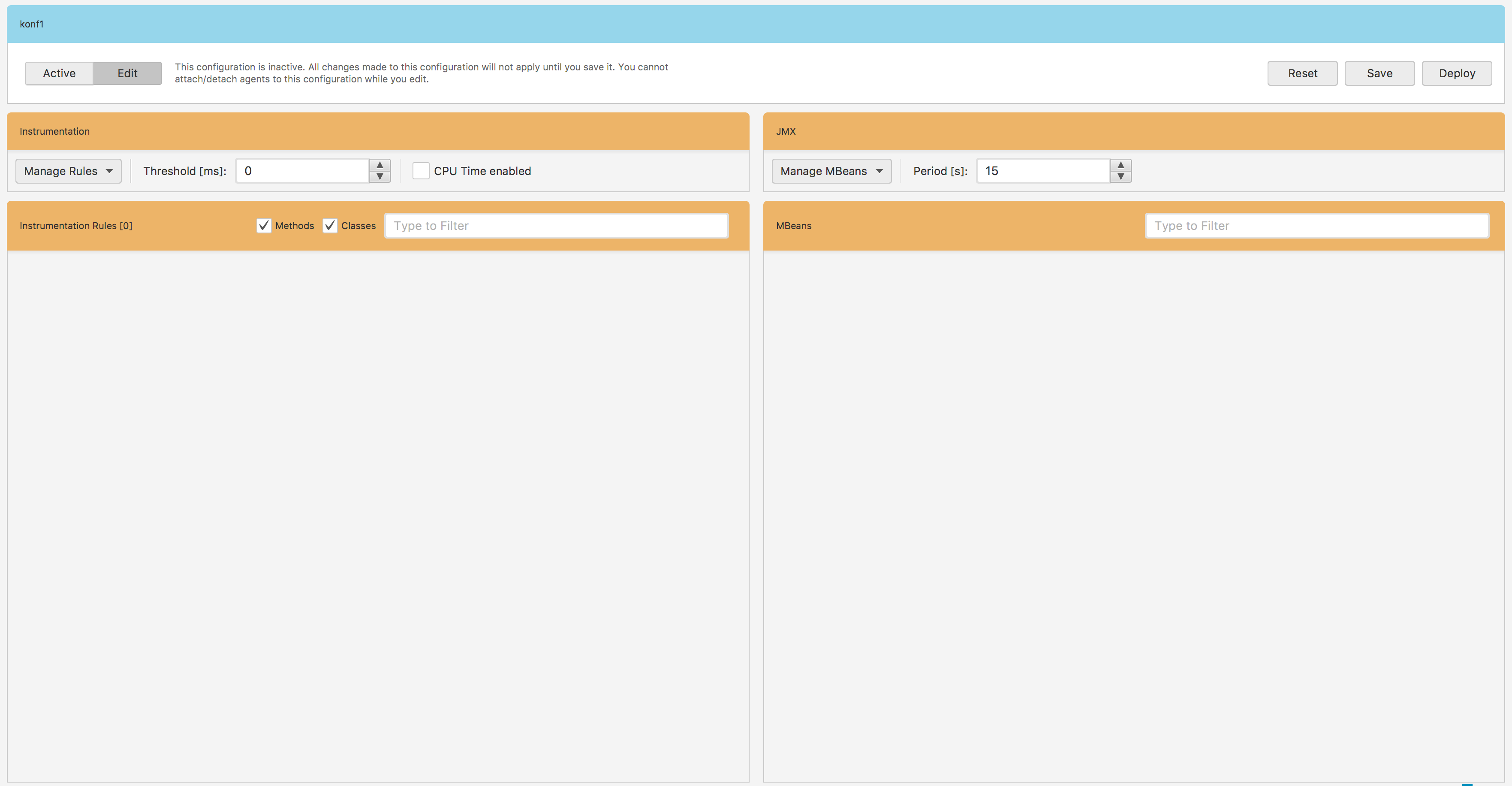
Fig. 1.9 Configuration Editor
The edit view Fig. 1.9 is divided into two parts. The left side is where you define instrumentation rules and the right one is where you define JMX beans to collect data from.
1.5.1. Instrumentation Rules¶
There are two entry fields in the top bar of the instrumentation part of the Fig. 1.9 view. In the Threshold field you can specify a threshold value for methods duration. In other words, you specify the lowest value of instrumented methods execution time above which these method calls will be reported. In the CPU Time enabled field you can select whether you want agents to report CPU time or not.
In order to add some rules, click the Manage Rules menu button Fig. 1.10.
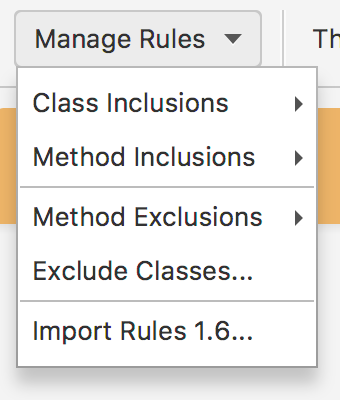
Fig. 1.10 Manage Rules Menu
Tip
You can import agents configurations from Flopsar 1.6, by clicking Import Rules 1.6… [1].
You have two types of rules at your disposal exclusions and inclusions and two levels of rules: class and method ones. Basically, you should specify at least one inclusion rule for classes and one for methods to have a valid configuration.
Excluding Classes
If you want to exclude some classes from the configuration, click the Exclude Classes… menu item. When a popup window appears, specify the pattern for fully qualified class names. If you specify the asterisk at the end, the rule will match every class, whose fully qualified name starts with the specified pattern. Otherwise, the exact match will be checked.
Including Classes
In order to determine which classes you want to instrument, you should select from the Class Inclusions submenu. If you want to match classes by their names, you should select the Add Class Rule… menu item. The same rules as above apply to the pattern of class names. If you want to instrument classes, which extend some super class, you should select the Add Super Class Rule… menu item. In this case you need to specify the fully qualified super class name. If you select the Entire Hierarchy checkbox additionally, every class which extends the specified super class will be instrumented regardless of its place in the inheritance hierarchy. Otherwise, only those classes will be instrumented, which extends the super class directly. If you want to instrument classes which implement some interface, you should select the Add Interface Rule… menu item. In the popup window you must specify a fully qualified name of the interface. Finally, if you want to instrument classes, which are annotated by some annotation, you should select the Add Annotation Rule… menu item. In the popup window you must specify a fully qualified name of the annotation.
Excluding Methods
When you are done with classes rules, you need to specify some method rules. If you want to exclude some methods from the configuration, you should select the Methods Exclusions submenu. If you do not want to instrument getter/setter methods, you should click the Exclude Accessors menu item. If you want to exclude some methods basing on their names, you should select the Exclude Methods… menu item. Here, you must specify a regular expression pattern for names. Finally, you can also exclude specific methods by selecting them from a list retrieved from running agents by clicking the Exclude from Hot Methods… (see Hot Methods for details).
Including Methods
Your final step is to define which methods instrument and how to do it. This can be achieved by selecting the Method Inclusions submenu. If you want to instrument methods with formatters, you should click the Add Formatter Rule…. This type of rule is created and edited in a popup window Fig. 1.11:
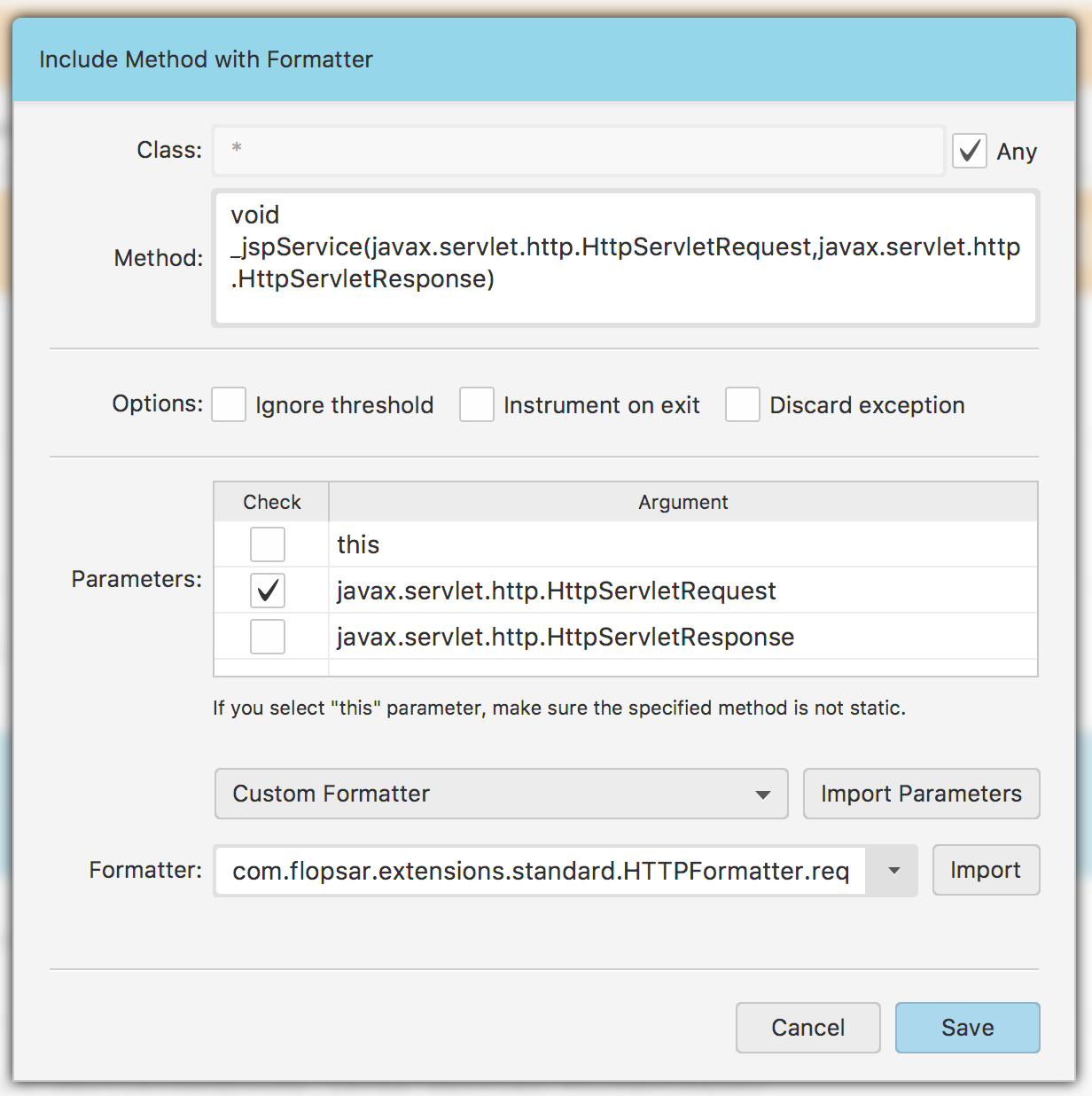
Fig. 1.11 Formatter Rule
There are some input fields that need to be filled. In the class field you can specify the exact class your instrumented method should belong to. If you do not want to determine the class, than you should select the Any checkbox. In the second text area field, you must specify the exact method signature you want to instrument. You should ignore arguments names and specify fully qualified class names of all objects. In the Options row you have three, additional options to select. If you want to ignore the configuration Threshold, select the Ignore threshold checkbox. If you want to instrument the method on exit, select the Instrument on exit checkbox. If you do not want the agent to report exceptions stack traces from this method, select the Discard exception checkbox. The Parameters table contains all your method arguments. You must populate this table by clicking the Import Parameters. This will import all the arguments from the method signature you specified above. Next, you should select which arguments you want the agent to pass to your formatter. You should also select which type of formatter you want to use: standard or custom. If you select the standard one, then you are done and you can click the Save button. If you select the custom formatter, you must then specify the formatter signature. There are two ways of specifying the formatter signature. The first one is to specify it manually by entering the signature in a form of class.method_name. The second one is used when you already have some implemented formatters. You just need to click the Import button and select a jar file with your formatters. The application will scan the jar and populate the formatters combo box with all the found and valid formatters. Select one of the formatters, click the Save button and you have your formatter rule created.
When you finished defining your configuration, you should get a similar view Fig. 1.12:
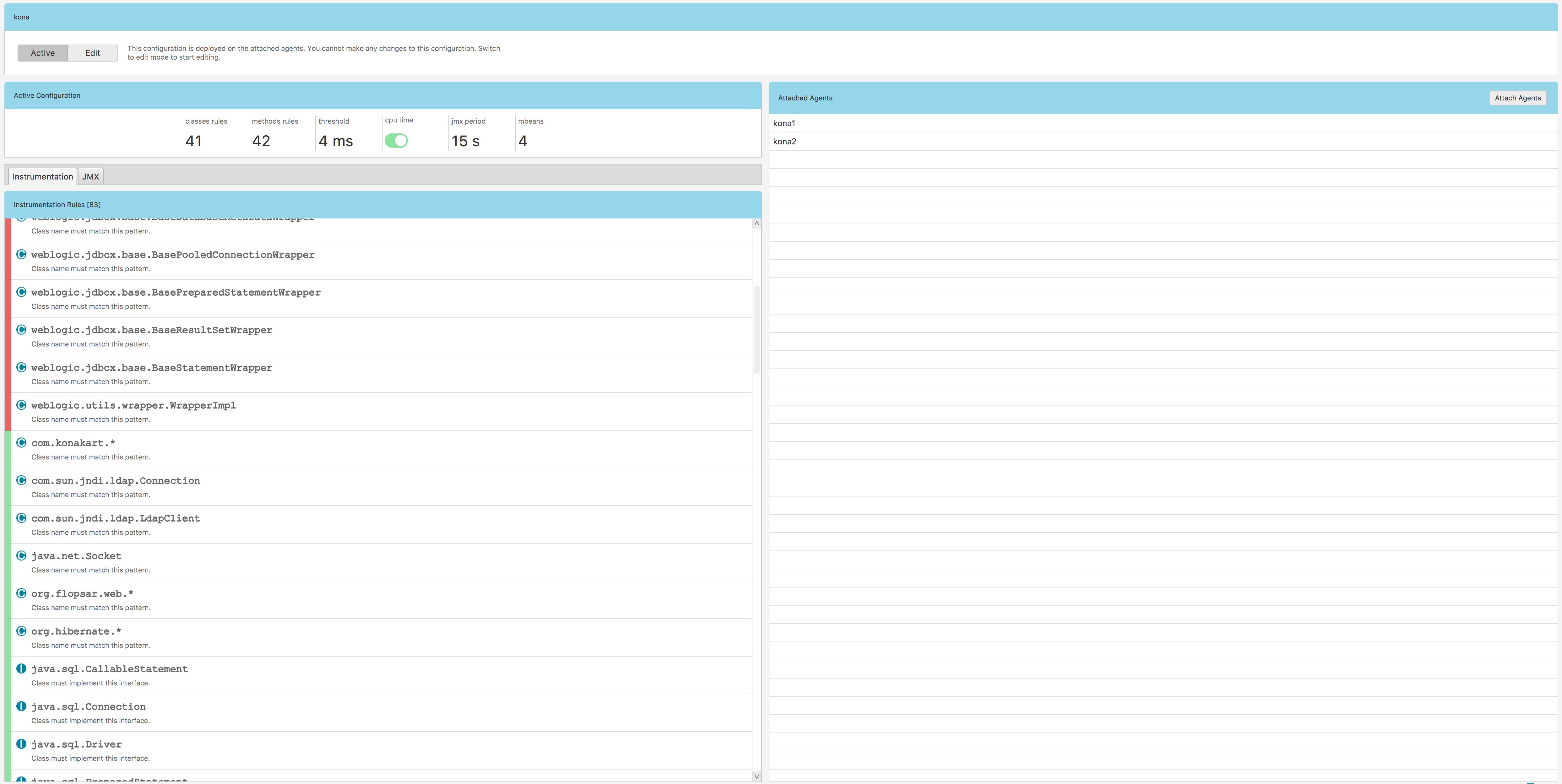
Fig. 1.12 Agent Configuration
There is either red or green bar at the beginning of each instrumentation rules entry. Exclusion rules are red and inclusion rules are green.
Footnotes
| [1] | This is a temporary feature and it will be removed in future releases. |
1.5.2. Hot Methods¶
This feature enables you to record instrumented methods executions. The Hot methods feature is very useful, when you tune your configuration for minimal performance impact. In this way, you can easily detect the most frequently executed methods and exclude them from instrumentation, unless you really need to instrument them. You can also exclude classes using this feature.
You can use this feature only when you have some agents attached to your configuration. In other words, agents are able to report their hot methods if and only if they instrumented these methods earlier. That means, you cannot use this feature when you create a new configuration and the configuration has not been deployed yet. You must first deploy the configuration, attach some agents to it and then edit the configuration again. Only then, this feature will be available to you.
In order to make use of Hot Methods, you should click the Exclude from Hot Methods… item from the Fig. 1.10 menu. A popup window Fig. 1.13 will appear then. If you cannot see any entries in the table, click the Collect button in the bottom-left corner. This will trigger an operation of retrieving hot methods from all the attached agents.
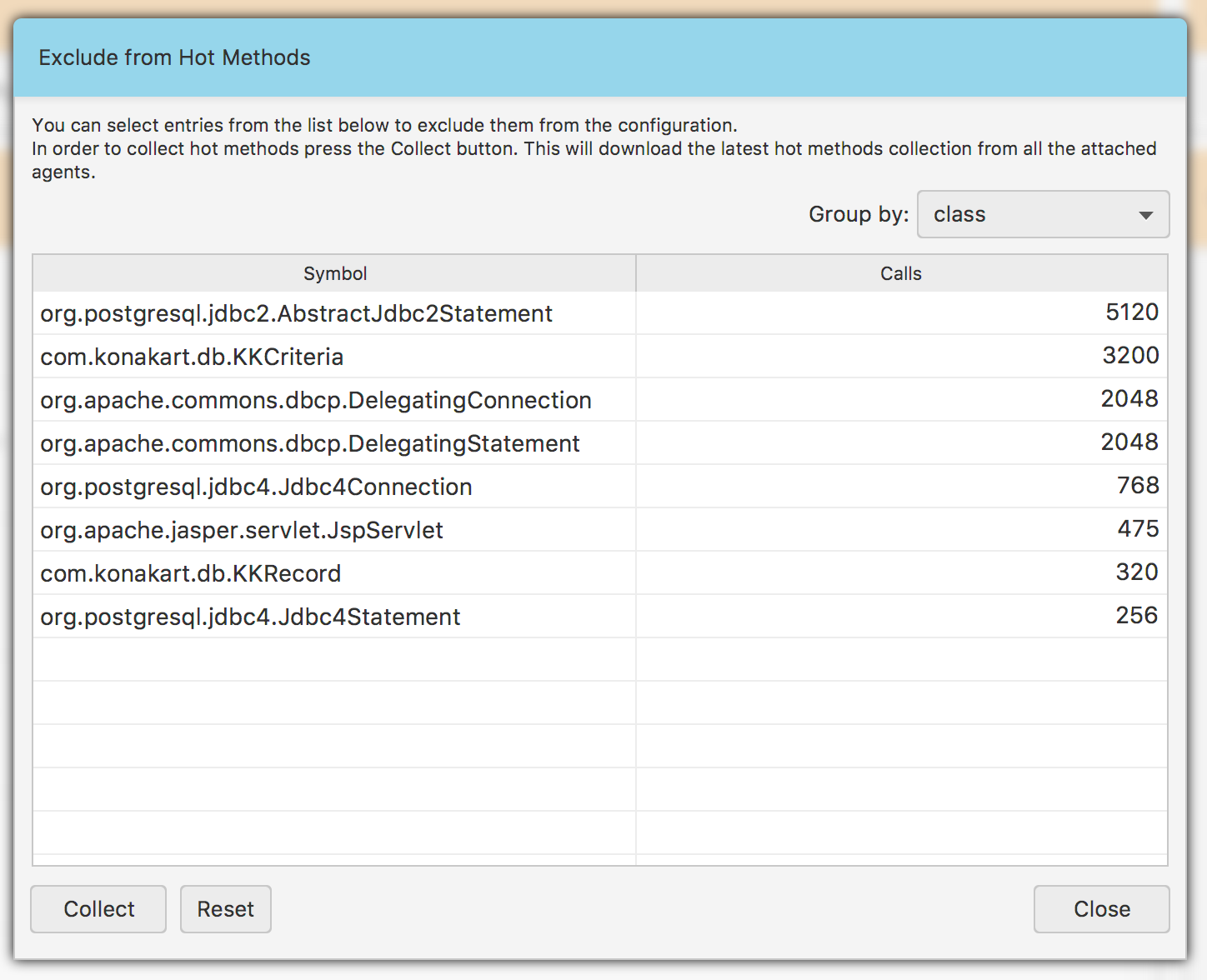
Fig. 1.13 Hot Methods
All the retrieved methods will populate the table Fig. 1.13. The results are always grouped by classes, methods, classes & methods or agents. You can exclude classes or methods only from views grouped by either emph{classes} or emph{methods} respectively. Views grouped by emph{classes & methods} and emph{agents} are only for information purposes. In order to exclude some entries, use a context menu over the table.
You can reset the results anytime and start to collect new results by clicking the Reset button. This will clear all the previous results and re-enable the Hot Methods feature on all the attached agents.
1.5.3. JMX¶
Configuring JMX for agents relies on specifying ObjectName patterns and the data collecting frequency. In the Period field you can specify how frequently agents must report data. In order to add some patterns, you must click the Manage MBeans menu. If you have your agent configuration from previous Flopsar versions, click the Import MBeans 1.6… [2] and select the configuration file.
Note
In order to add new ObjectName patterns, you must have some configuration deployed and some agents attached.
Adding new patterns requires you to deploy some configuration and attach some agents in the first place. MBeans can be imported only from running agents, so there must be some agents attached to the configuration. Assuming your setup fullfills the aforementioned conditions, click the Import MBeans… menu item. You should get a popup window with a list of available ObjectNames Fig. 1.14.
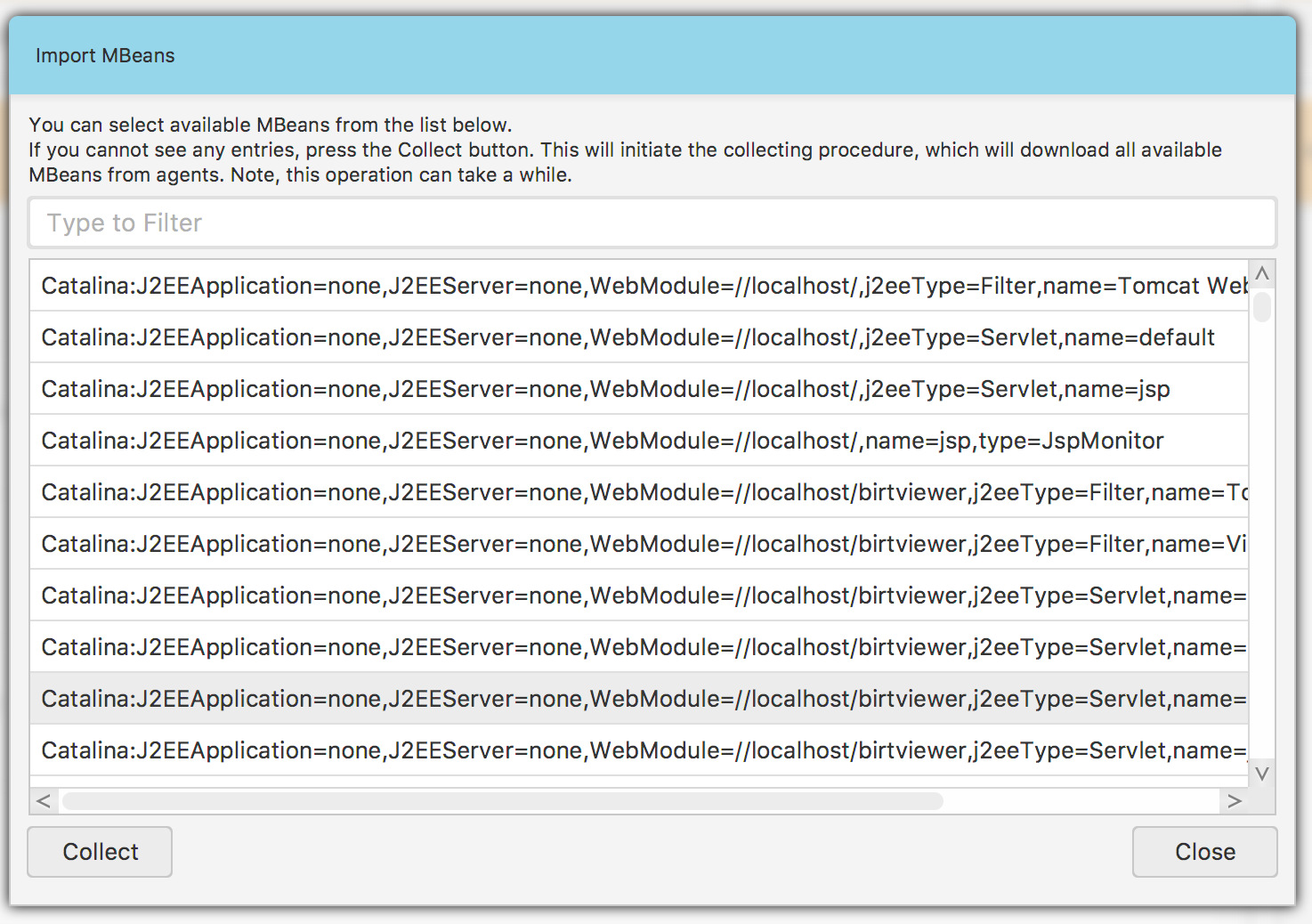
Fig. 1.14 Importing JMX ObjectNames
If the list is empty, click the Collect button in the bottom-left corner. This operation will collect all the available ObjectNames from all the attached agents. In order to add some selected record, either double-click the record or use the list context menu. When you are done with importing ObjectNames, click the Close button. Now, you should have the selected records added to the MBeans list in the Fig. 1.9 view.
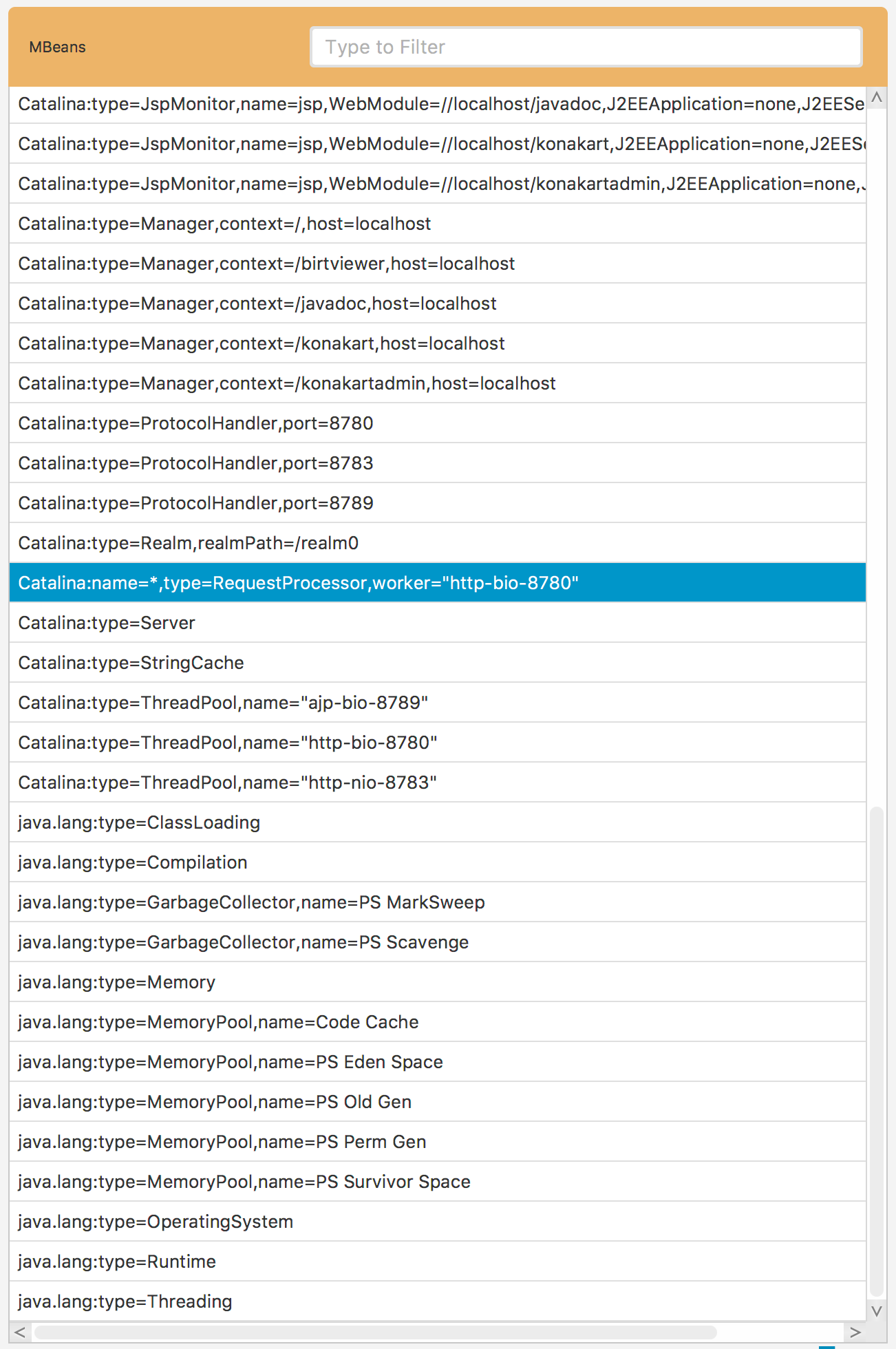
Usually, most of ObjectNames is specific to the servers they come from. Their names contain a server specific data such as IP addresses, ports etc. That means there are ObjectNames that are available only on particular servers. In order to make them available on most of the servers and simplify the configuration we need to modify their ObjectNames. This can be achieved by clicking the Transform to Pattern… menu item in the list context menu. As a result you should get a similar popup window to this one Fig. 1.15.
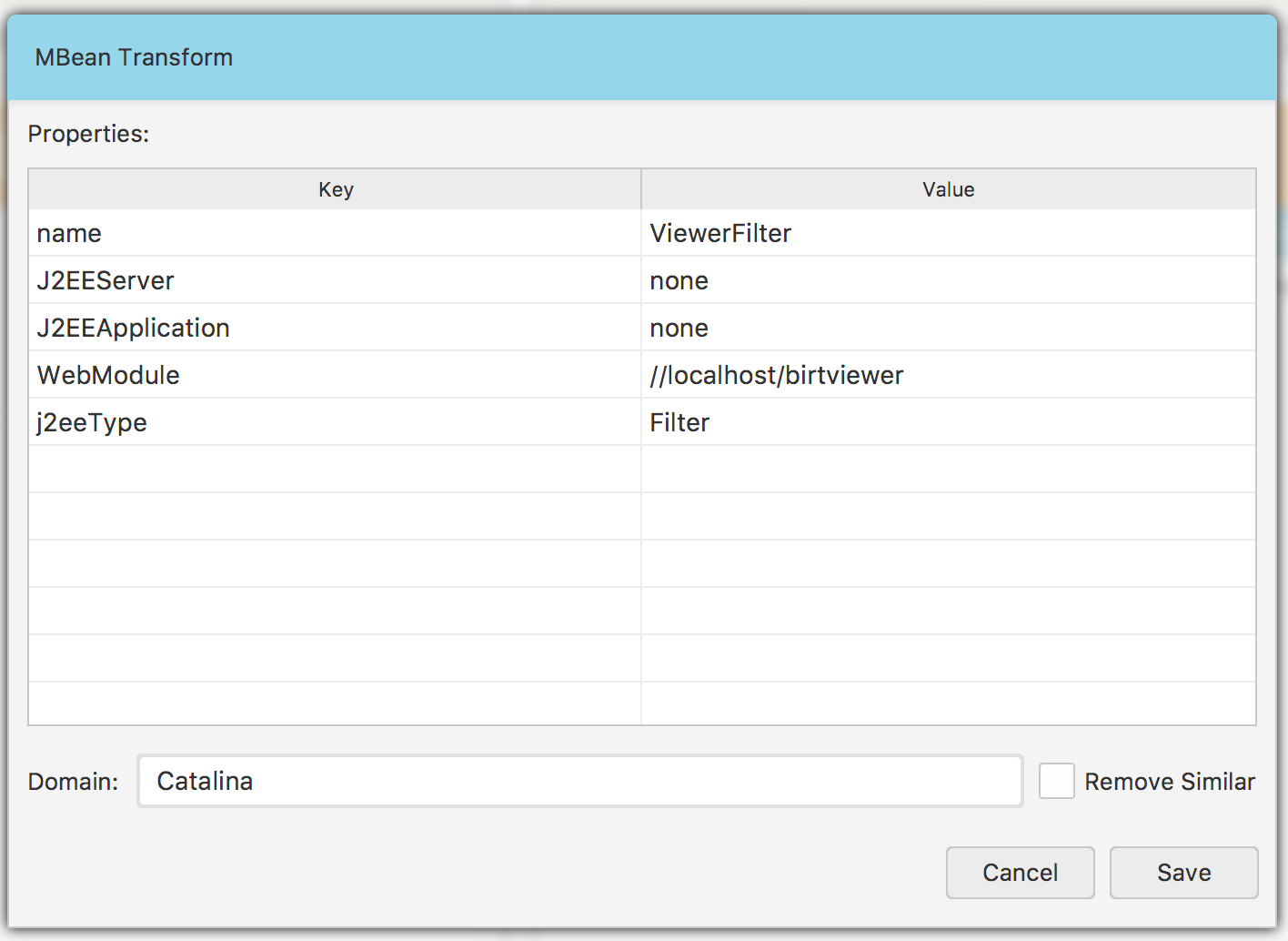
Fig. 1.15 Transforming ObjectName
This is a view of a decomposed ObjectName into keys and values. The Value column is editable so that you can replace values with custom ones and transform some specific ObjectName into a pattern. In order to edit the values just double-click the record and modify it. The Remove similar checkbox is used if you want to get rid of other, similar ObjectNames, whose name matches your pattern.
In order to illustrate the transformation procedure see Fig. 1.16. There are multiple ObjectNames, which are very similar and the only key they differ is the name. By transforming the name value to * of just one of these similar records, we can easily simplify the entire set of similar records into a single ObjectName. That is exactly how the transformation procedure works.
1.5.4. Deploying Agents Configurations¶
When your configuration is ready to be deployed, you should first save it by clicking the Save button in Fig. 1.9. This operation will only persist the configuration in the manager.
Warning
If you do not save your configuration before you exit workstation, all the changes you made will be lost.
In order to activate the configuration, you must click the Deploy button. This operation will make the configuration you saved active. This will also notify all the attached agents about it and upload the configuration to all of them. The agents will check whether there are any changes between their current configuration and the new one. If the agents detect instrumentation rules changes, they will reload their configuration. The reloading operation duration can vary and it strongly depends on the configuration and application itself. It can take from a few seconds to a minute.
Warning
Configuration reloading is a heavy operation and will degrade your application performance temporarily. It can even halt the entire application for the time of reloading operation. Do not reload a configuration when your application is under heavy load.
Footnotes
| [2] | This is a temporary feature and it will be removed in future releases. |
1.6. Galaxies¶
Galaxies are special views of collected data. Basically, this is an alternative view of stacks executions, where stacks are represented as dots. We distinguish two kinds of the views, i.e. historical and online ones.
1.6.1. Online Galaxy¶
The online galaxy is used to monitor recent 15 minutes of selected agent instances. They can be managed from the galaxy explorer Fig. 1.18.
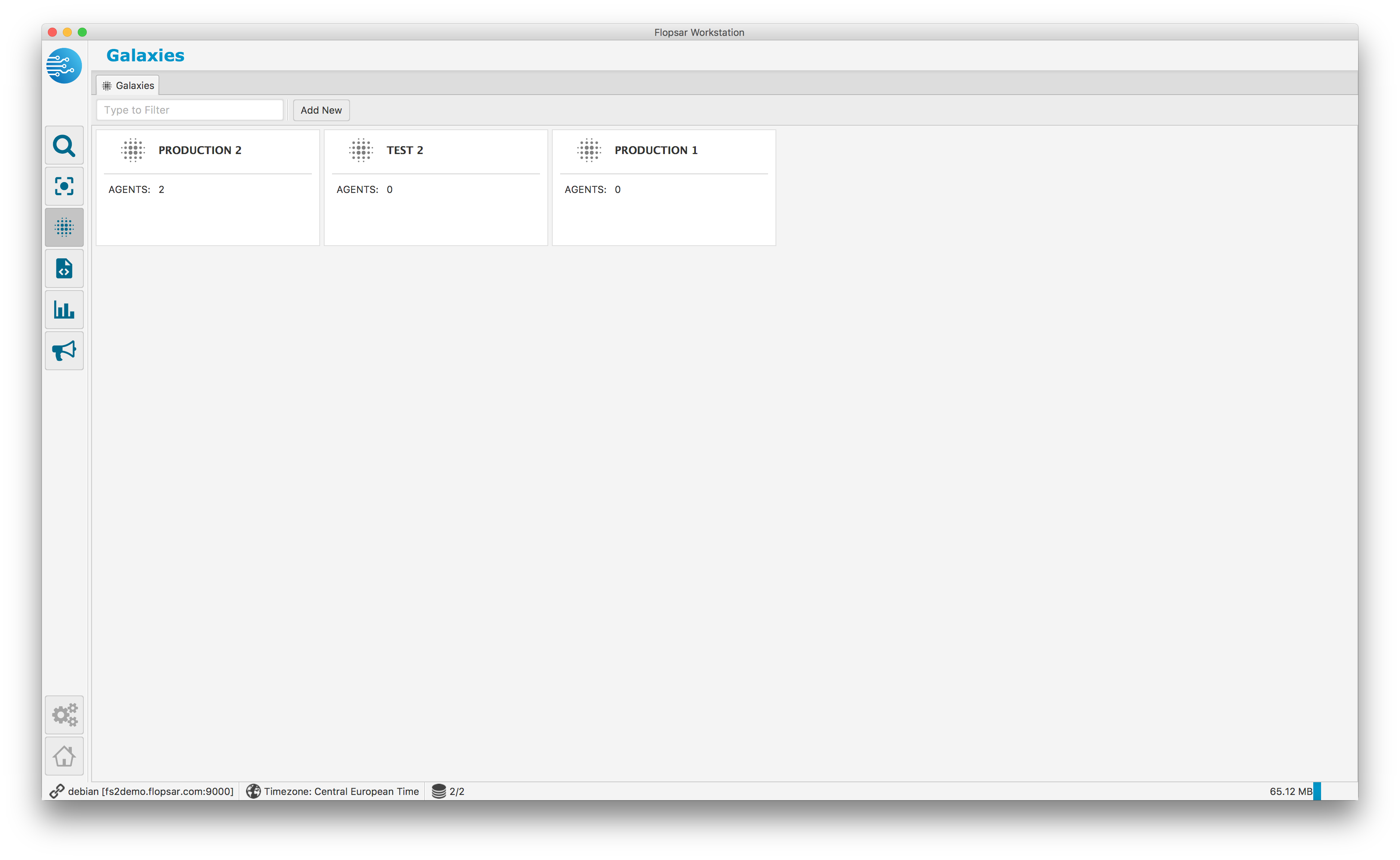
Fig. 1.18 Galaxies Explorer
Each tile represents a single galaxy view. The AGENTS label on tiles represents the number of agents currently attached to corresponding galaxies. A new galaxy can be added by double-clicking the Add New button. You can see the galaxy details Fig. 1.19 by double-clicking the corresponding tile.
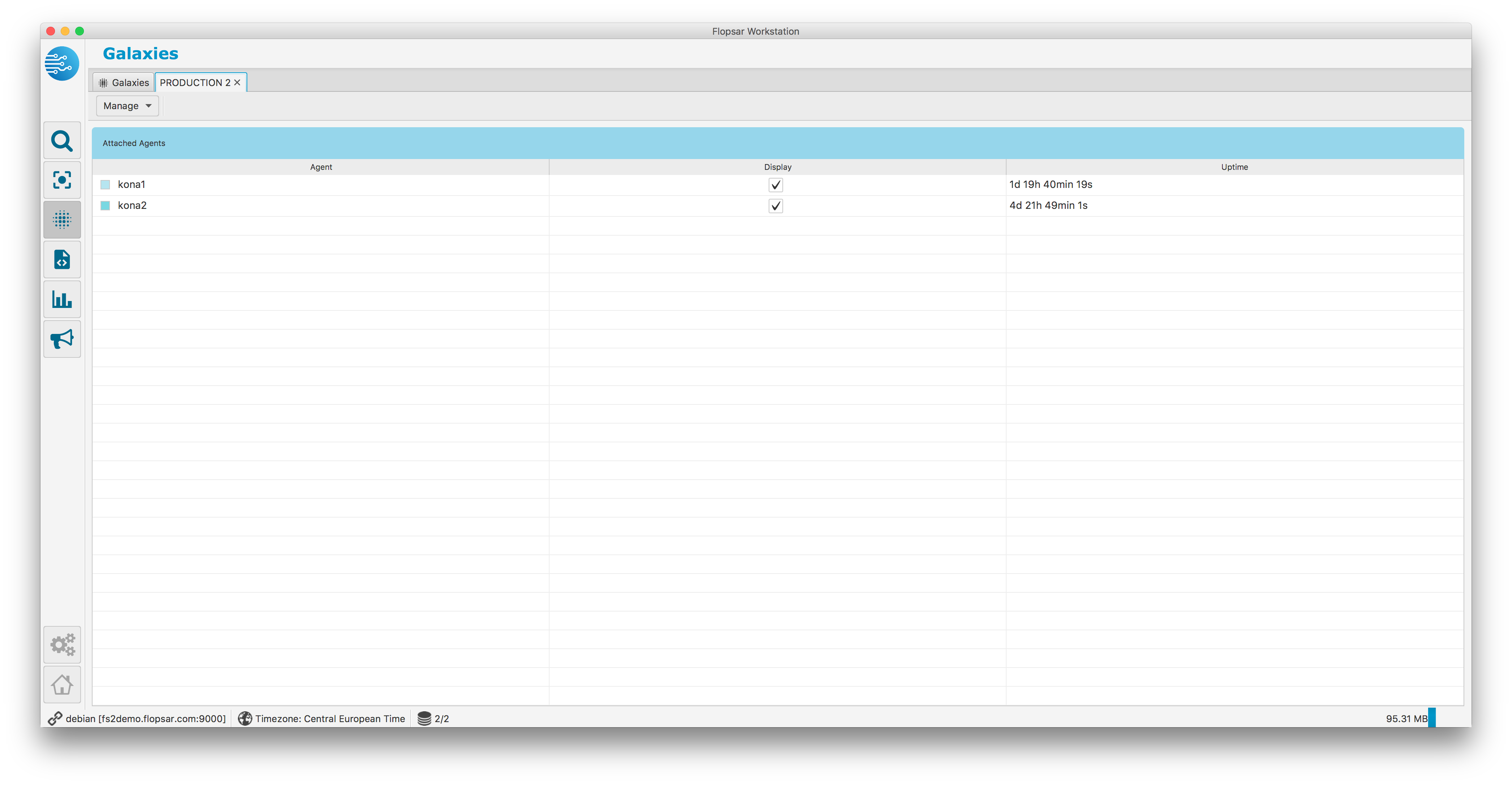
Fig. 1.19 Galaxy Details
This view contains a table with three columns. There is an agent name along with a small, colored square in the first column. The color of the square is used to distinguish among various agents on the galaxy view. If you want to change the color, just click the square. The second column is editable and allows you to decide whether you want the agent to be displayed on the galaxy view. The third column shows the current uptime of the agent. If you want to open the galaxy view Fig. 1.20, just click the menu item Manage –> Show.
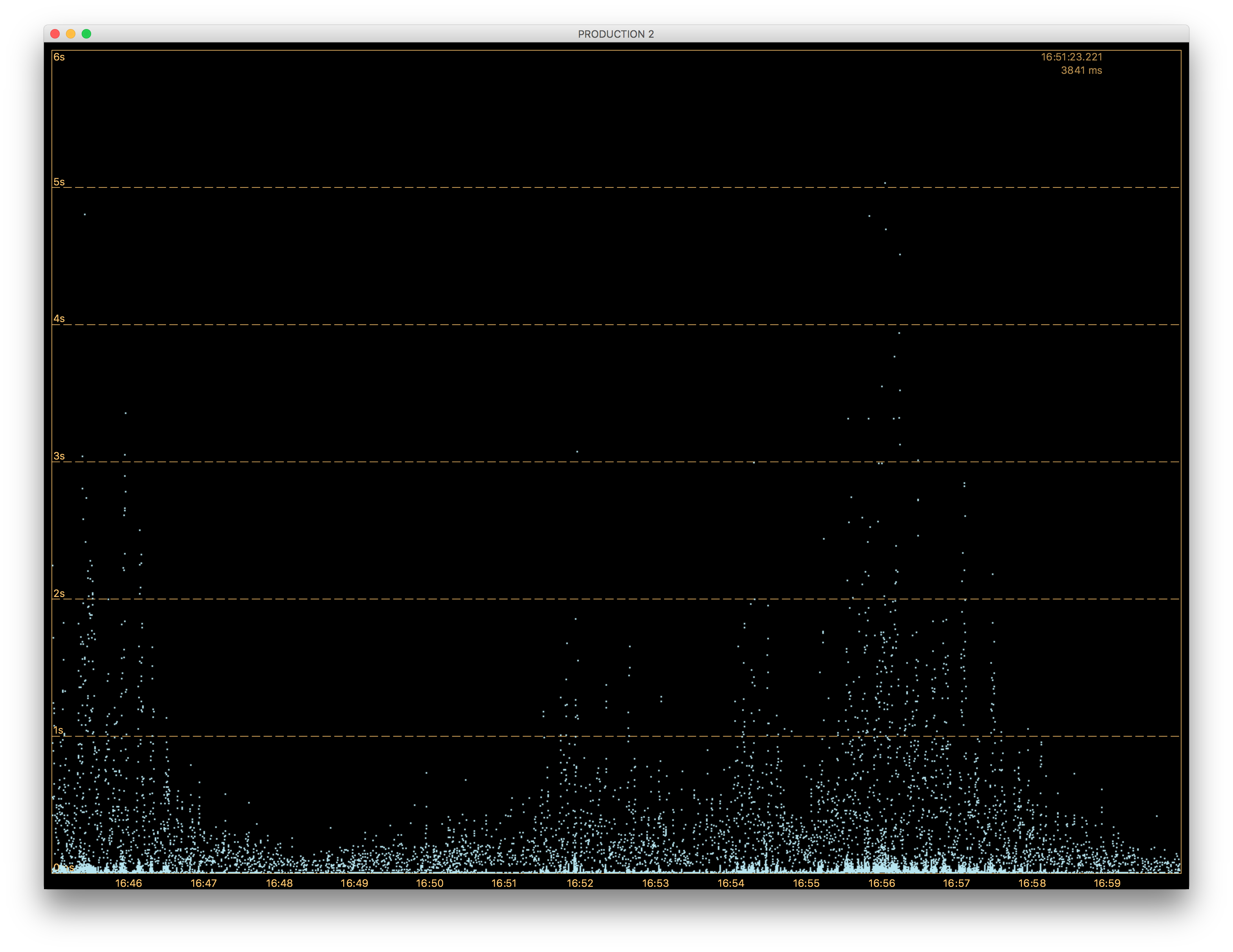
Fig. 1.20 Galaxy View
This is a live view of your attached agents. Each dot represents a single method execution. The method duration is displayed on the vertical axis. The horizontal axis shows a time axis and the whole view moves from right to the left as time goes by. If you want to change the graph scale, you can use your mouse scroll. In order to customize the graph, use its context menu Fig. 1.21.
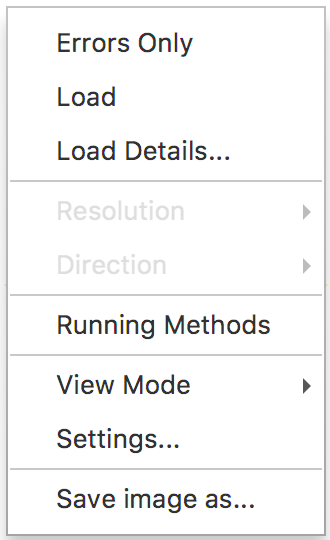
Fig. 1.21 Galaxy Context Menu
The context menu has several options, which enable you to customize your galaxy. It also provides auxiliary information about your data reported by the agents. If you want to see the total load of the attached agents, select the Load checkbox item. It will display a stacked area graph of the load for all the attached agents Fig. 1.22. The bottom area denotes those calls which threw exceptions. When the load is displayed, the number of total calls is displayed in the veritcal axis on the ride side of the graph.
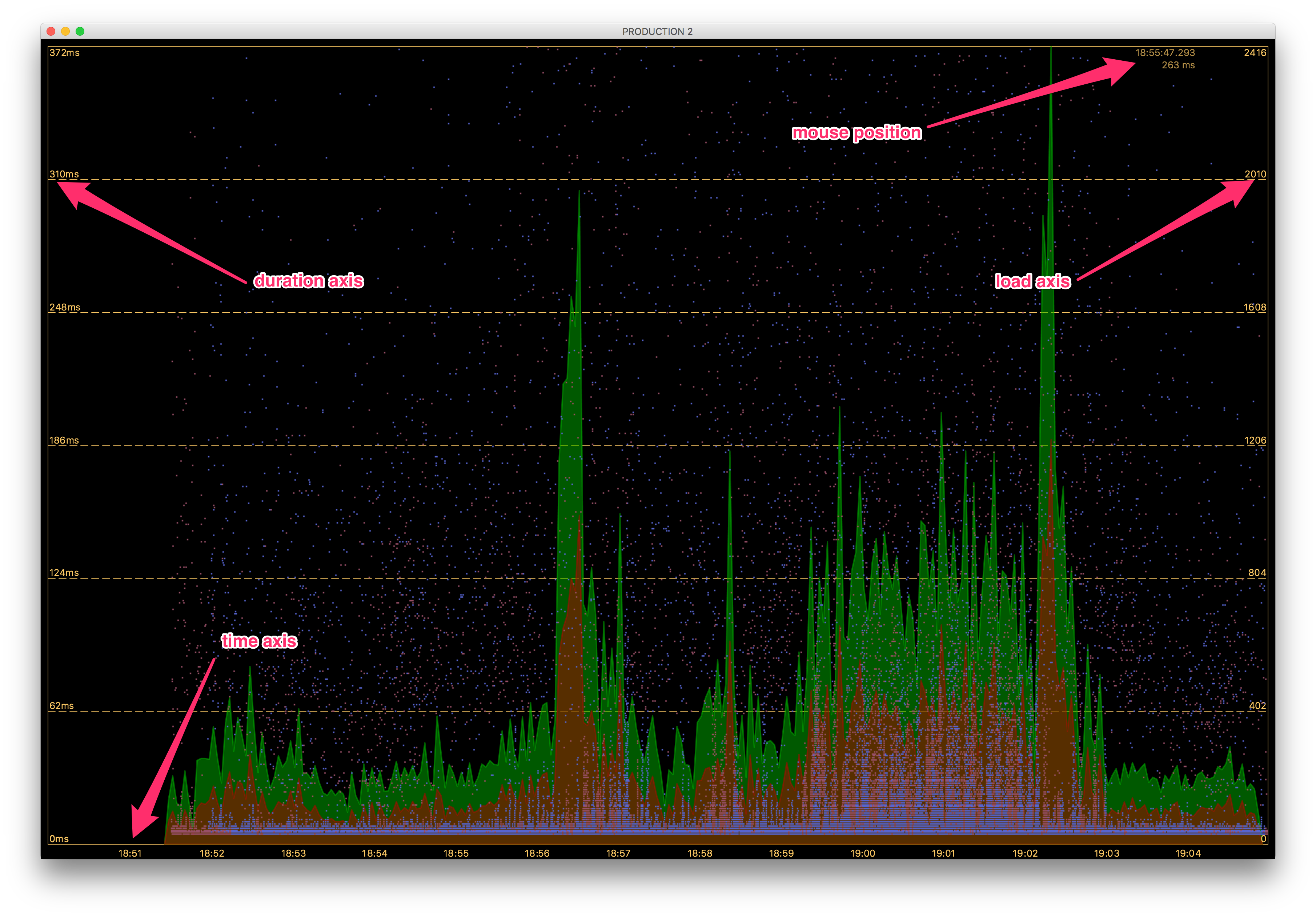
Fig. 1.22 Galaxy View: Load
This load view is an aggregated one so if you want to see how the load looks for each agent, click the Load details… menu item. You should see a view Fig. 1.23 with the table and the graph on it. The Errors column shows the total number of calls that threw exceptions. The Calls column shows the total number of calls.
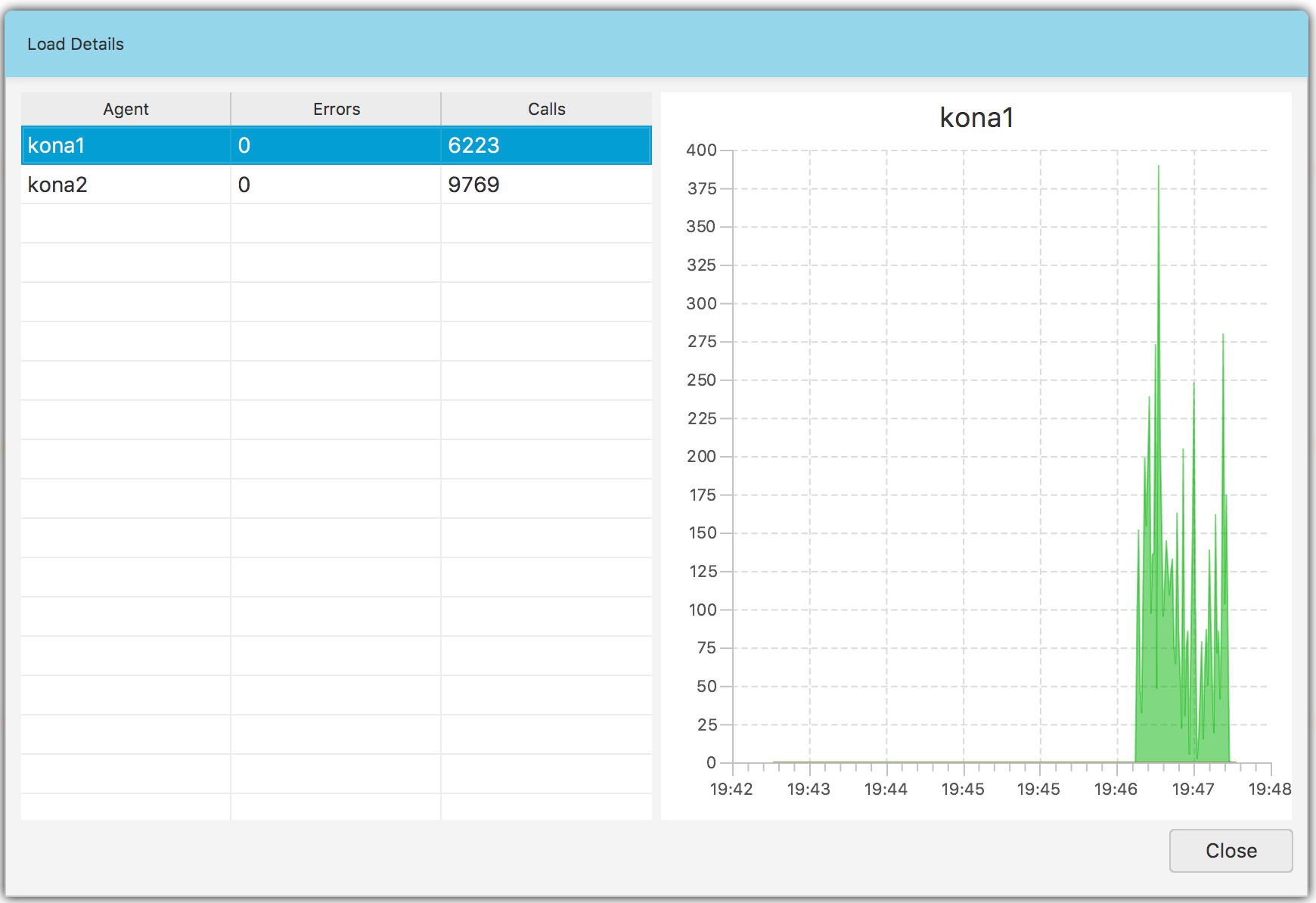
Fig. 1.23 Galaxy View: Load per Agent
If you want to customize some galaxy colors and scale, click the Settings… menu item. In the settings window Fig. 1.24 you can change background, selection, load backgrounds colors. You can also change the duration range on the vertical axis.
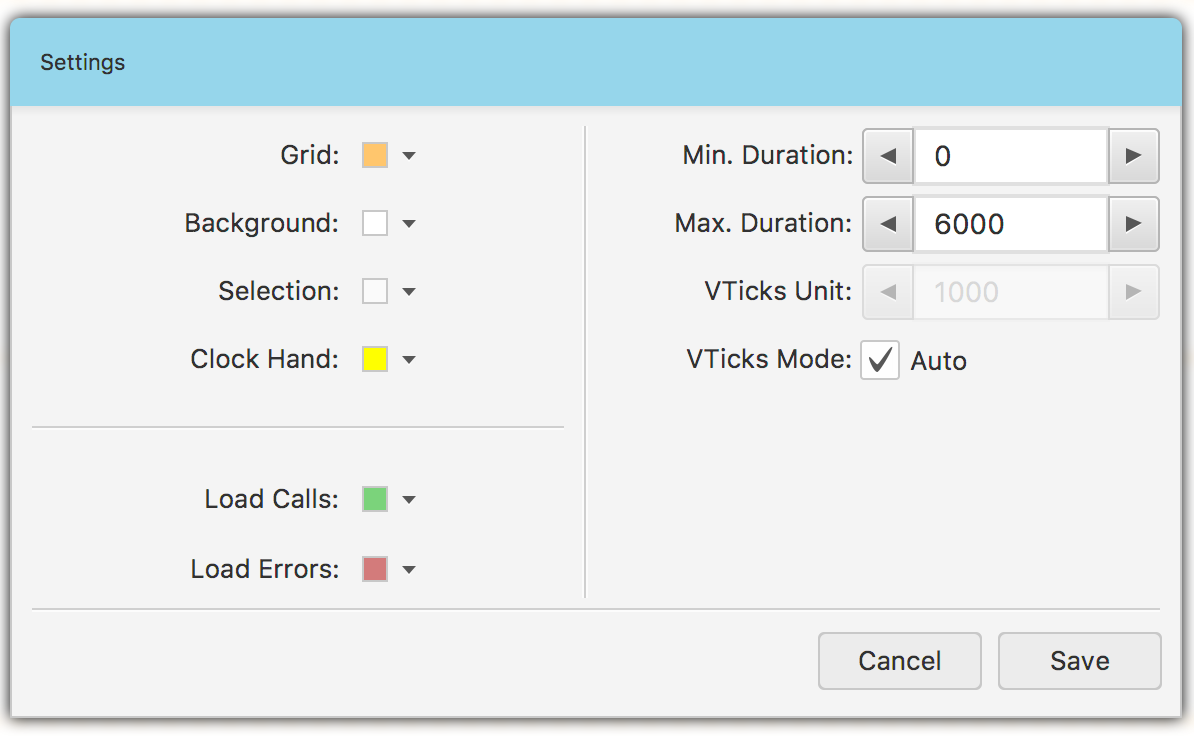
Fig. 1.24 Galaxy View Settings
Your can switch between two types of galaxies: flat and radar ones. If you want to switch to the radar Fig. 1.25, select the View Mode –> Radar menu item.
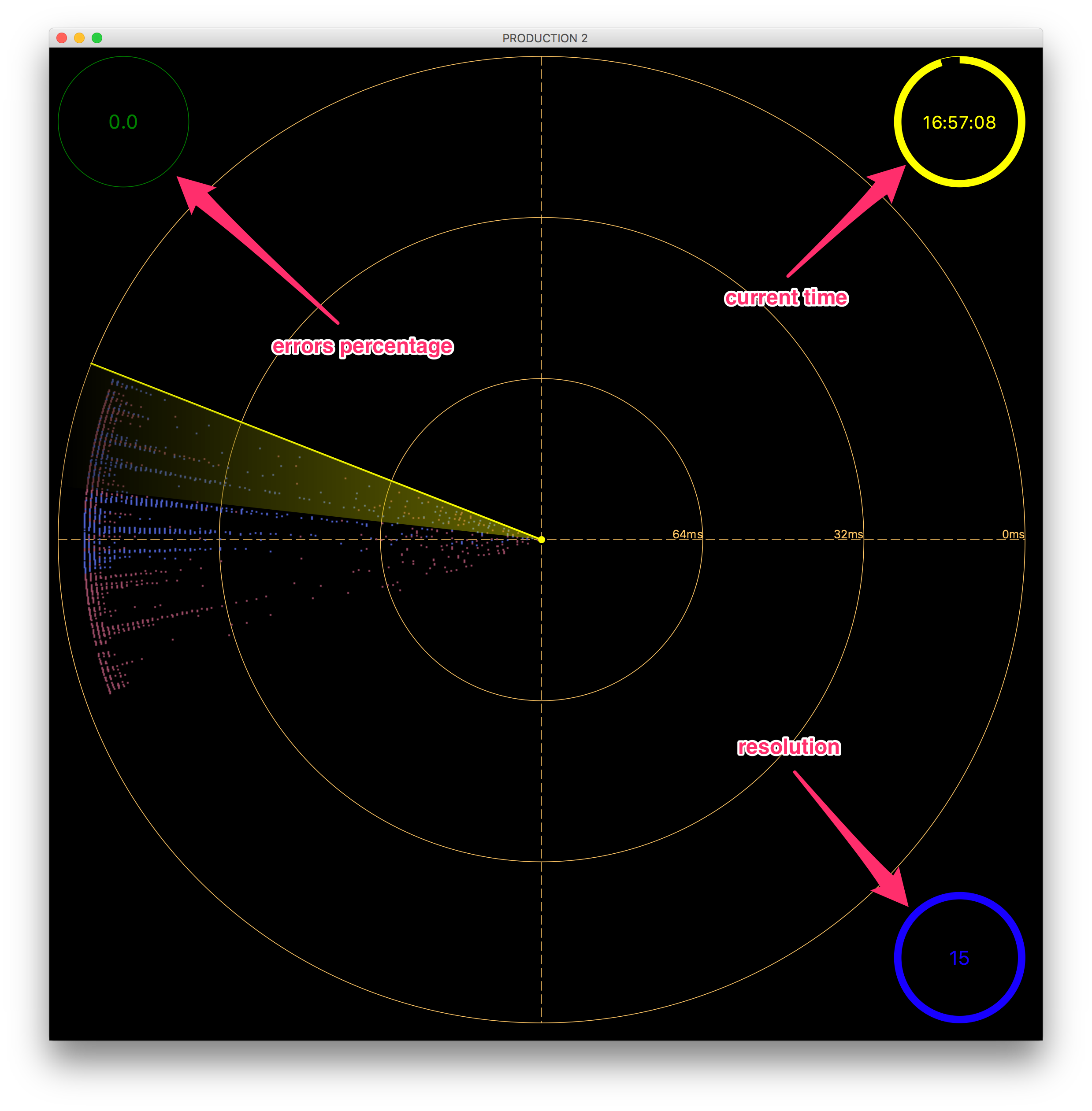
Fig. 1.25 Galaxy View: Radar
If you want to display only those method calls, which throw exception then select the Errors only checkbox item.
Galaxy Radar
1.6.2. Historical Galaxy¶
Unlike the online galaxy a historical one is used to analyze historical data, which satisfy some conditions specified in the search form. In order to display the results in a galaxy form, you must select the Galaxy mode in the search form Fig. 1.26.
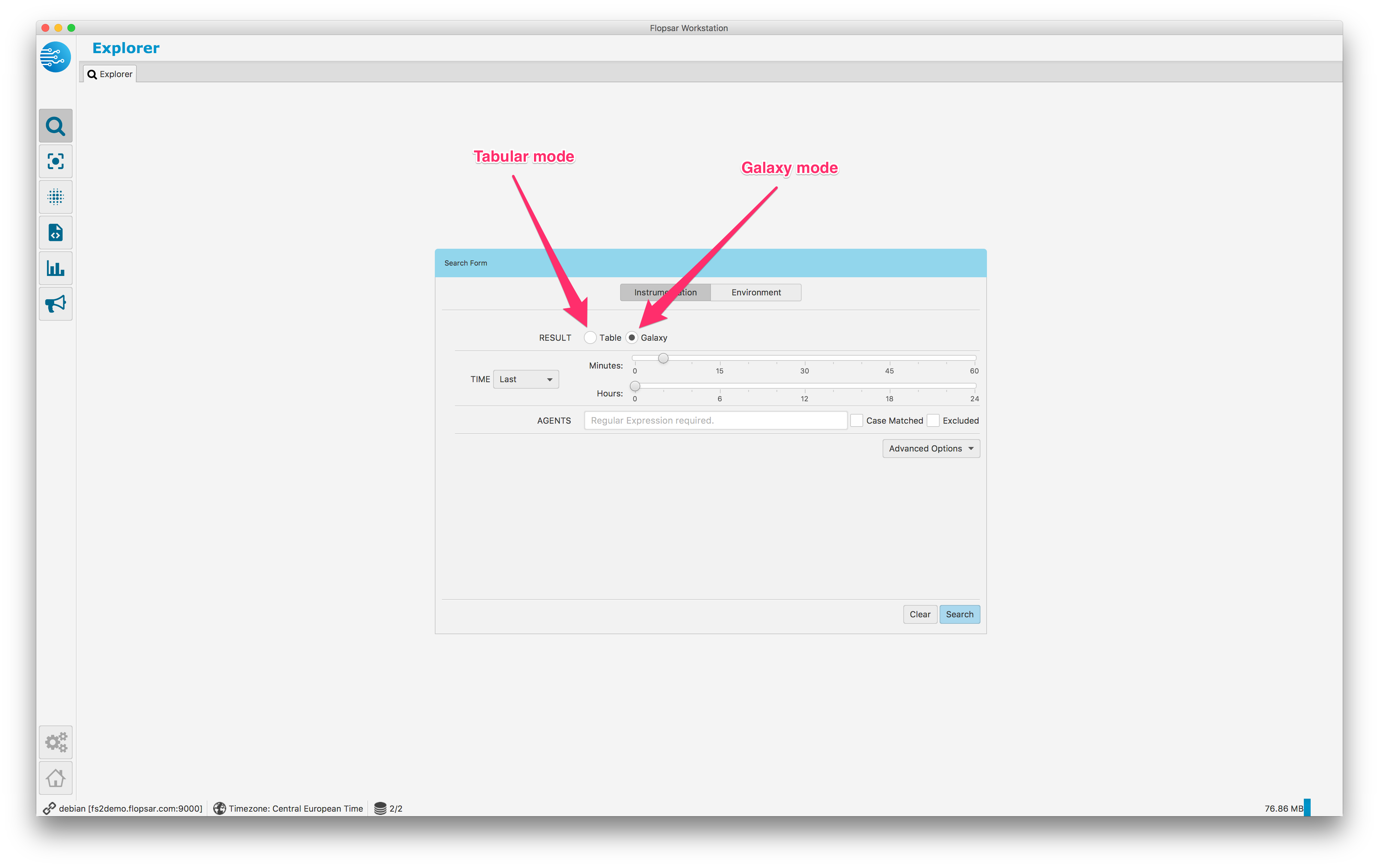
Fig. 1.26 Data Explorer Search Form
When you click the Search button, you should get a similar result to Fig. 1.27. The view is divided into two regions. The left view presents your query results in a form of galaxy. The right view contains a table of those agents, whose data are displayed on the galaxy. In the first column, there is an agent name and its color. You can change this color by clicking the small square and selecting a new color. In the second column, you can either show or hide the data corresponding to the selected agent. The third column contains a total share of calls of the corresponding agent on the galaxy. The last column contains a total share of exceptions throws by calls of the corresponding agent. You can either show or hide this table by clicking on the toggle button Agents in the right-top corner of the view.
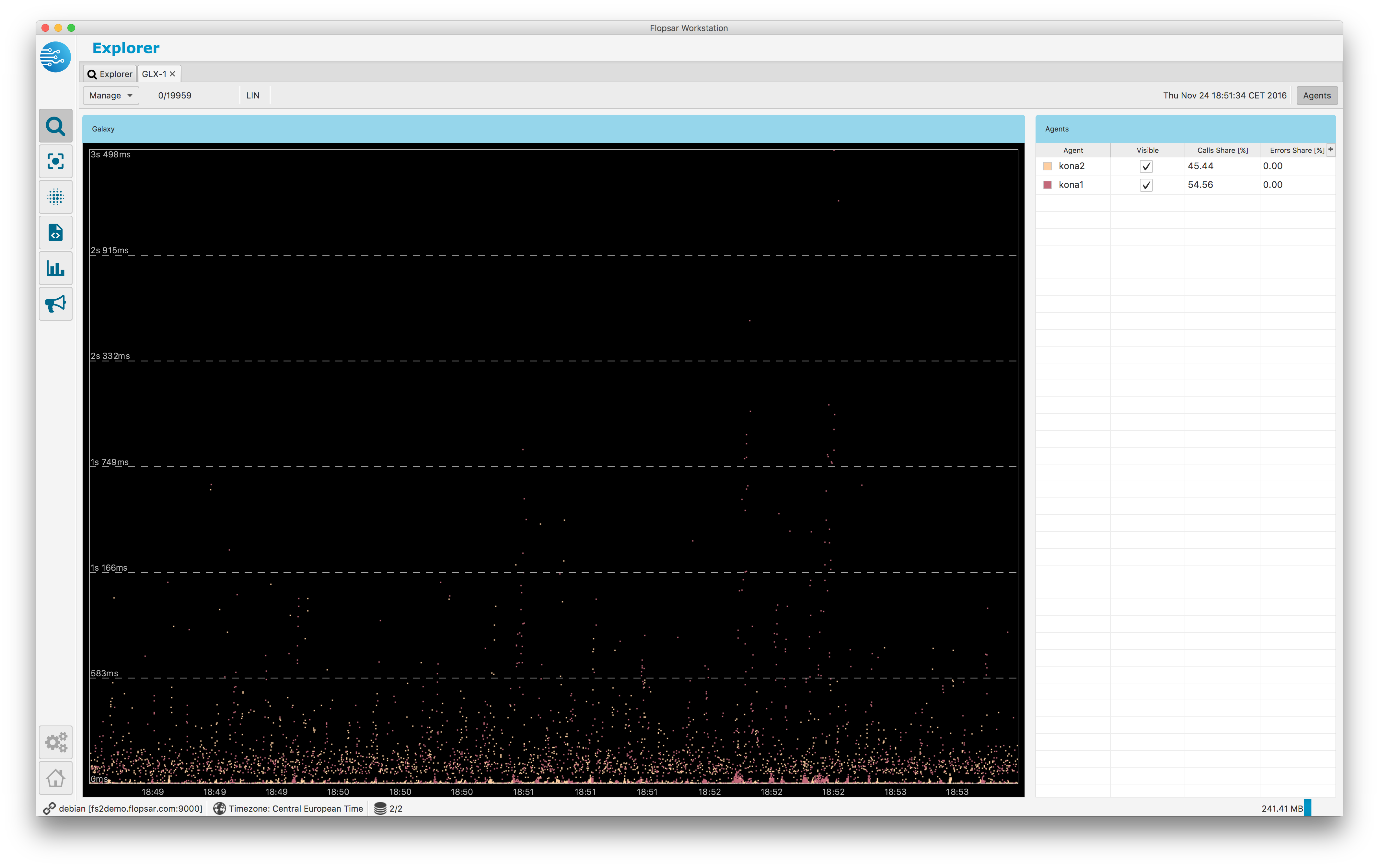
Fig. 1.27 Galaxy Result
The galaxy context menu Fig. 1.28 allows you to extend the analysis. If you select the Load menu item, you will get the load view in a form of a stacked area graph. The area colors correspond to the agents data. When the load is displayed, the calls count values are displayed on the right vertical axis.
Fig. 1.28 Galaxy Result Context Menu
Using the Scale submenu you can change the graph scale which can be either linear or logarithmic. If you click the Settings menu item you can change the galaxy background and foreground colors.
If you want to find out what method calls are displayed, just click and drag your mouse to create a rectangle which covers the area you are interested in. If you release the mouse button, you will be taken to the tabular mode where the calls will be presented to you.
Besides, the galaxy flat view, your query results can be presented in a form of galaxy clock view Fig. 1.29. The view projects data onto a clock face. You can see only data from twelve hours range at a time. Use the AM, PM radio buttons and the date picker to change time.
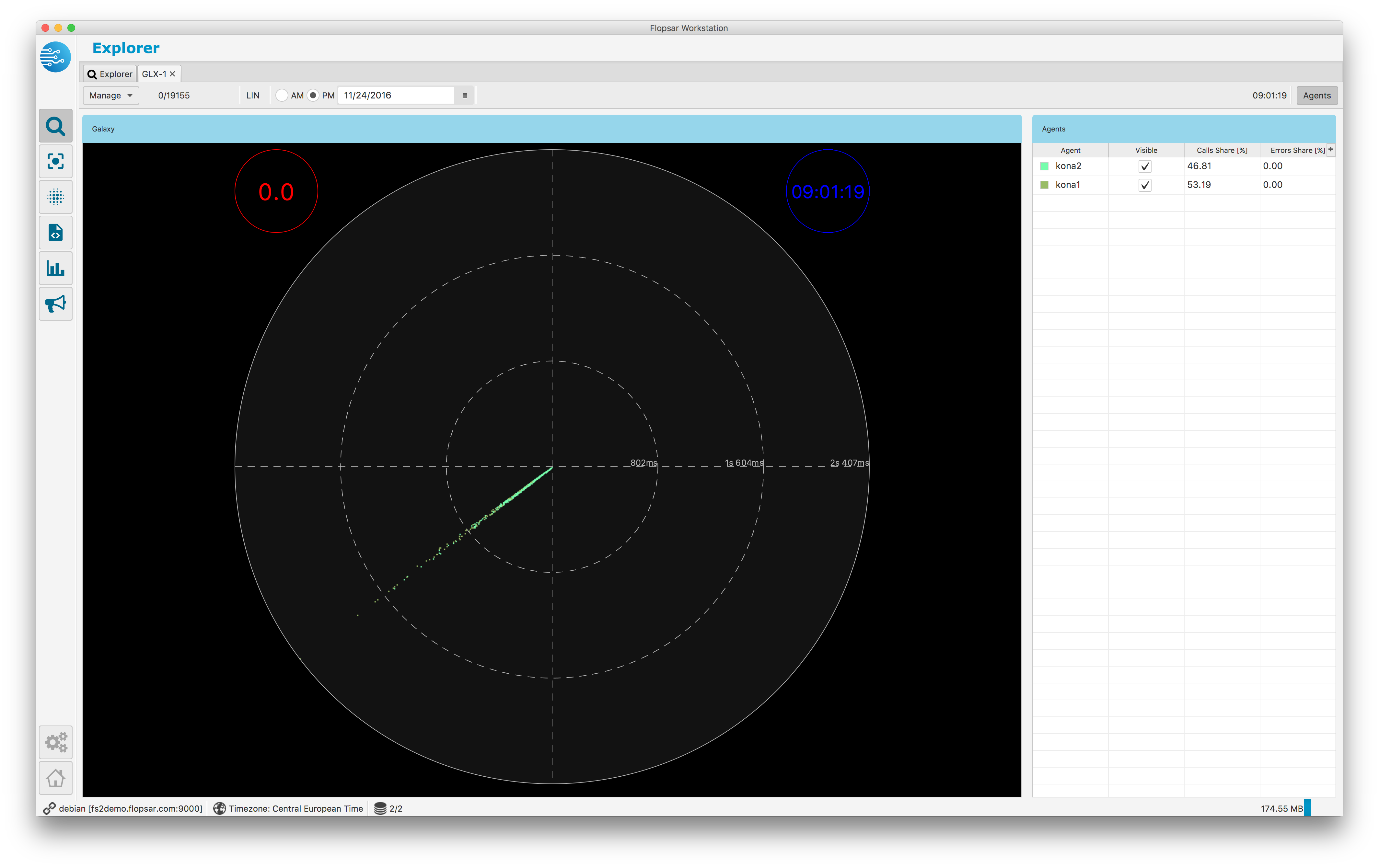
Fig. 1.29 Galaxy Clock View
Additionally, there are two extra views available. They can be displayed by clicking the Manage –> Switch View submenu and selecting one of the available items. If the Duration Distribution item is selected, Fig. 1.31 view will be displayed. If the Calls Distribution is selected, Fig. 1.30 view will be displayed.
Calls Distribution
This stacked-bar chart Fig. 1.30 presents methods calls distribution with respect to duration. Each color represents a single agent. The y-axis presents the number of calls. You can adjust both bar width (in milliseconds) and duration range (in milliseconds).
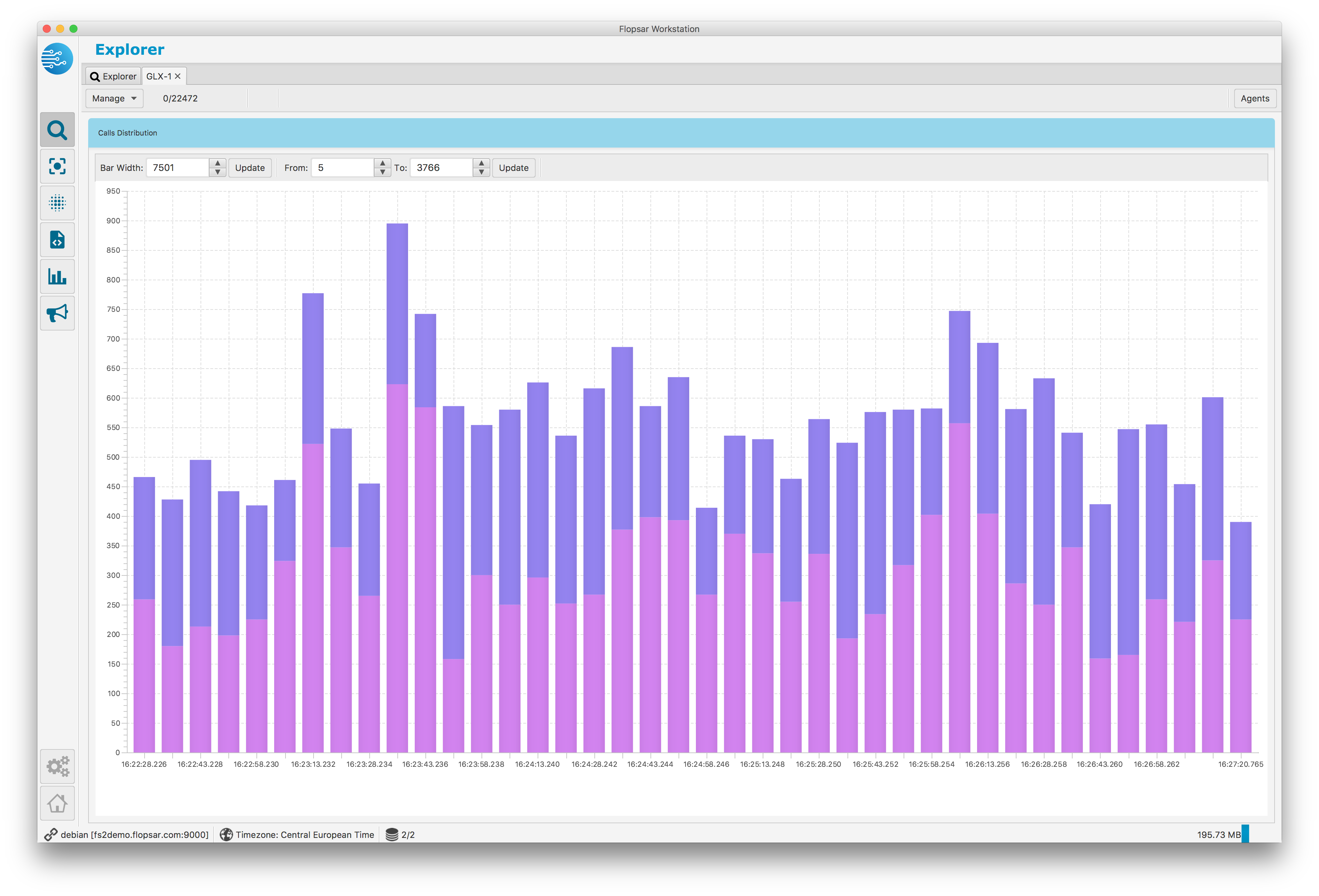
Fig. 1.30 Galaxy Calls Distribution
Duration Distribution
This stacked-bar chart Fig. 1.31 presents methods duration distribution with respect to time. Each color represents a single agent. The y-axis presents the number of calls. You can adjust both bar width (in milliseconds) and duration range (in milliseconds).
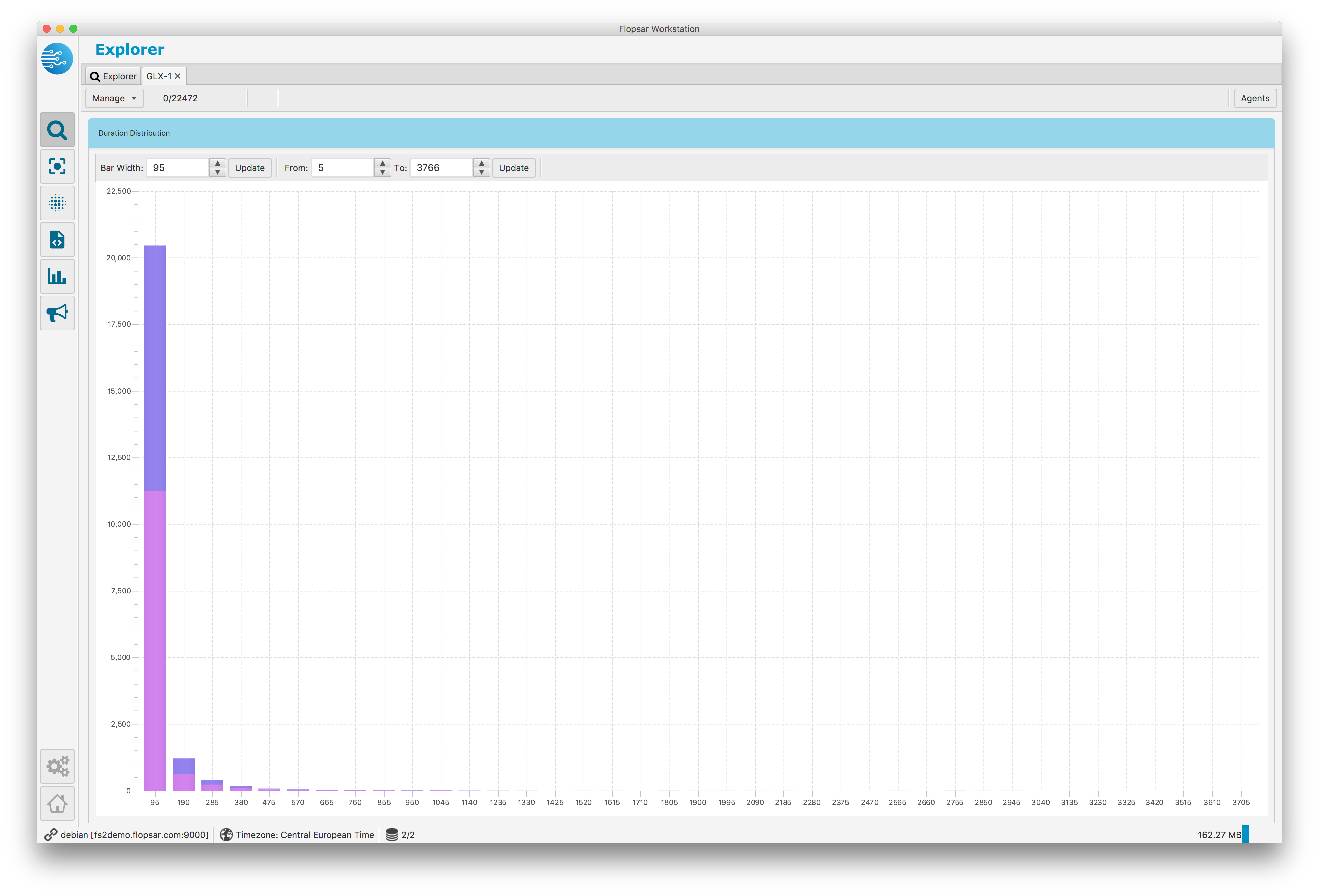
Fig. 1.31 Galaxy Duration Distribution
When you double-click on a bar in either Fig. 1.30 or Fig. 1.31, you will get a view Fig. 1.32, with list of methods from this bar.
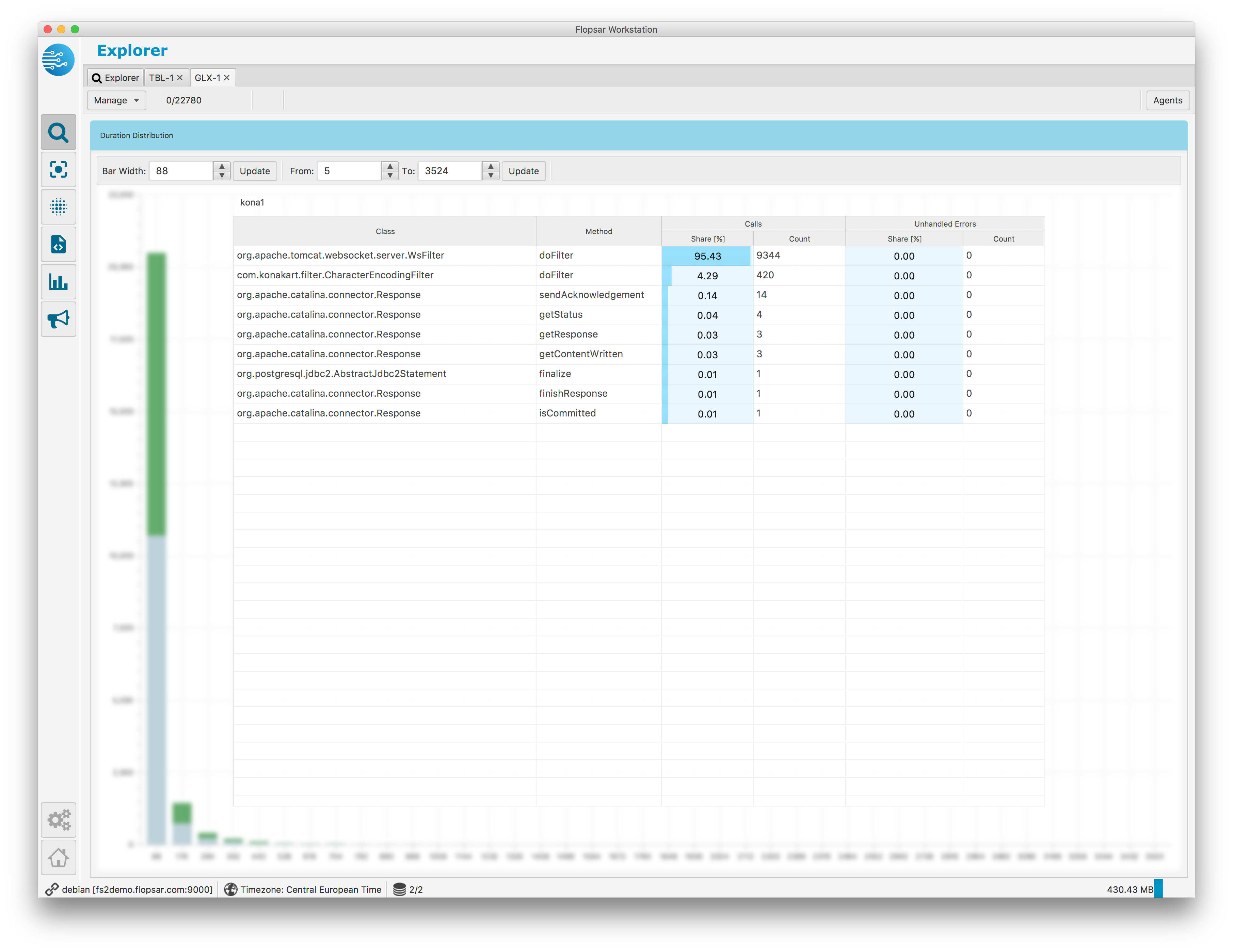
Fig. 1.32 Galaxy Duration Distribution: Bar Content
1.7. Exploring Instrumentation Data¶
If you click Data Explorer tile in Fig. 1.3 you should obtain the view Fig. 1.33. This view has a search form in the center. The search form is used to explore both instrumentation and environment data. For instrumentation data toggle Instrumentation button and for environment data toggle the other one.
In order to explore instrumentation data, you need to fill the search form (Fig. 1.26). First, in the RESULT row you must select which type of result you want to get. If you want to explore tabular data, then you must select Table. If you want to get the result in a form of galaxy view, you must select Galaxy. The second row TIME enables you to specify a time range. You can choose either sliders to set the time range quickly or date time pickers to specify a custom range. The AGENTS entry, requires you to specify a regular expression for an agent name (5 recent entries are always stored in the entry).
Tip
When you click the AGENTS label, a popup window will appear. This window contains a list of all available agents. If you click one of the agents from this list, its name will be copied to the AGENTS entry field.
If you are done, you can simply click the Search button.
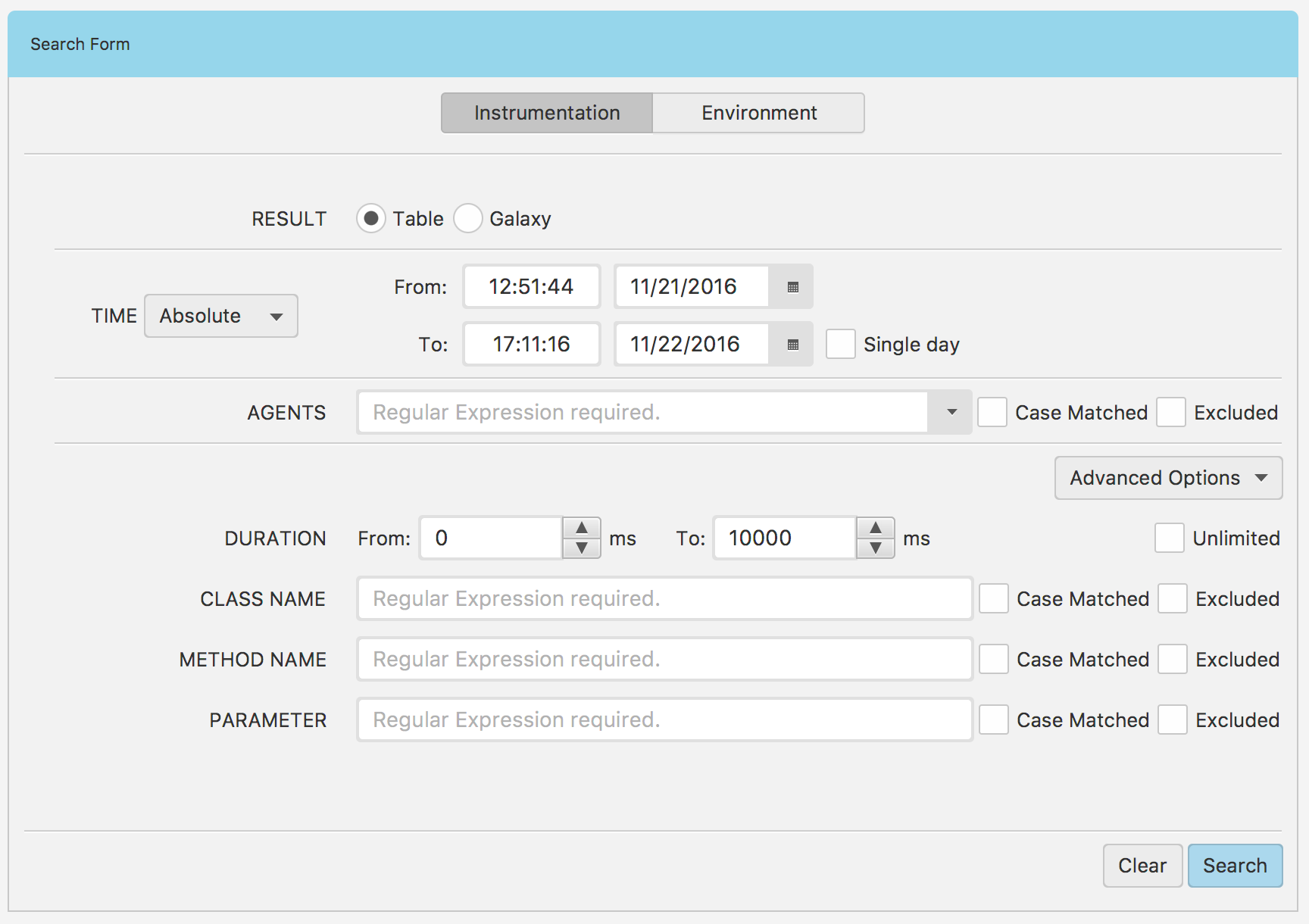
Fig. 1.33 Instrumentation Expanded Form
If you want to narrow your search results, you can use Advanced Options menu to specify additional conditions (Fig. 1.33). The DURATION row enables you to specify a duration range. In the CLASS NAME entry you can specify a regular expression pattern for a class name. In the METHOD NAME entry you can specify a regular expression pattern for a method name, and finally in the PARAMETER entry you can set a regular expression for a parameter. Each additional condition will narrow your search results. This means that only those results will be returned which satisfy all the specified conditions.
When you click the Search button, you should see the similar view to Fig. 1.34, provided that you selected the Table result type.
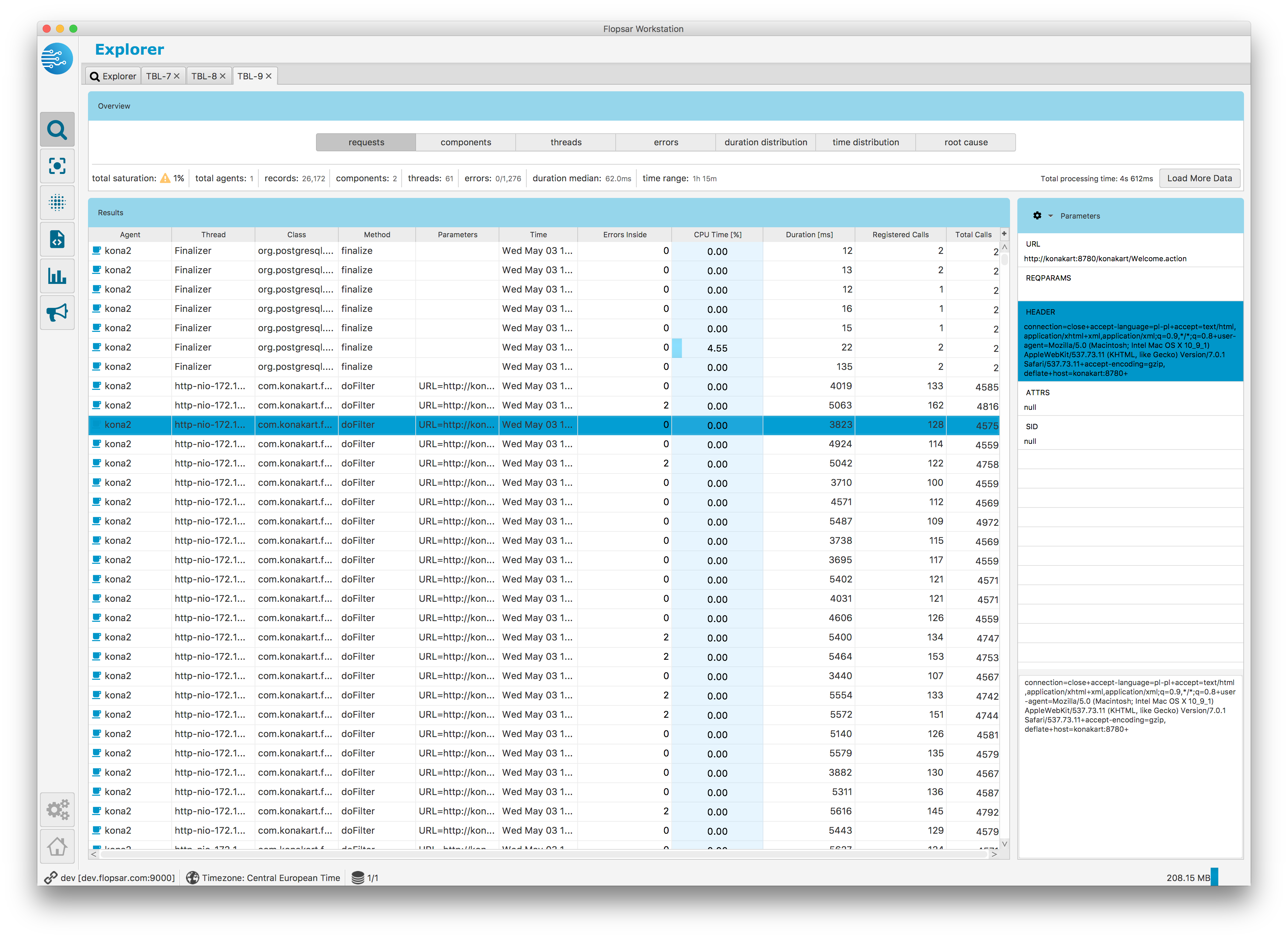
Fig. 1.34 Table results: Records View
Each time when you search instrumentation data you receive only a part of the response data. If you get more, you must click the Load More Data button. You can repeat this procedure to receive more data until the button changes its label to No More Data.
Formatting Parameters
1.7.1. Execution Stack Interpretation¶
When you double-click on some selected record in table Fig. 1.34, you will get a window Fig. 1.35 with this record details. The window presents a tree representing an execution stack of the selected method call. This tree view is self-explanatory but there can be situations where this view can be a bit confusing. This can happen when the displayed execution stack does not exactly correspond to the execution flow you see in your application source code. In order to understand why this situation takes place you must understand how the execution stack tree is built.
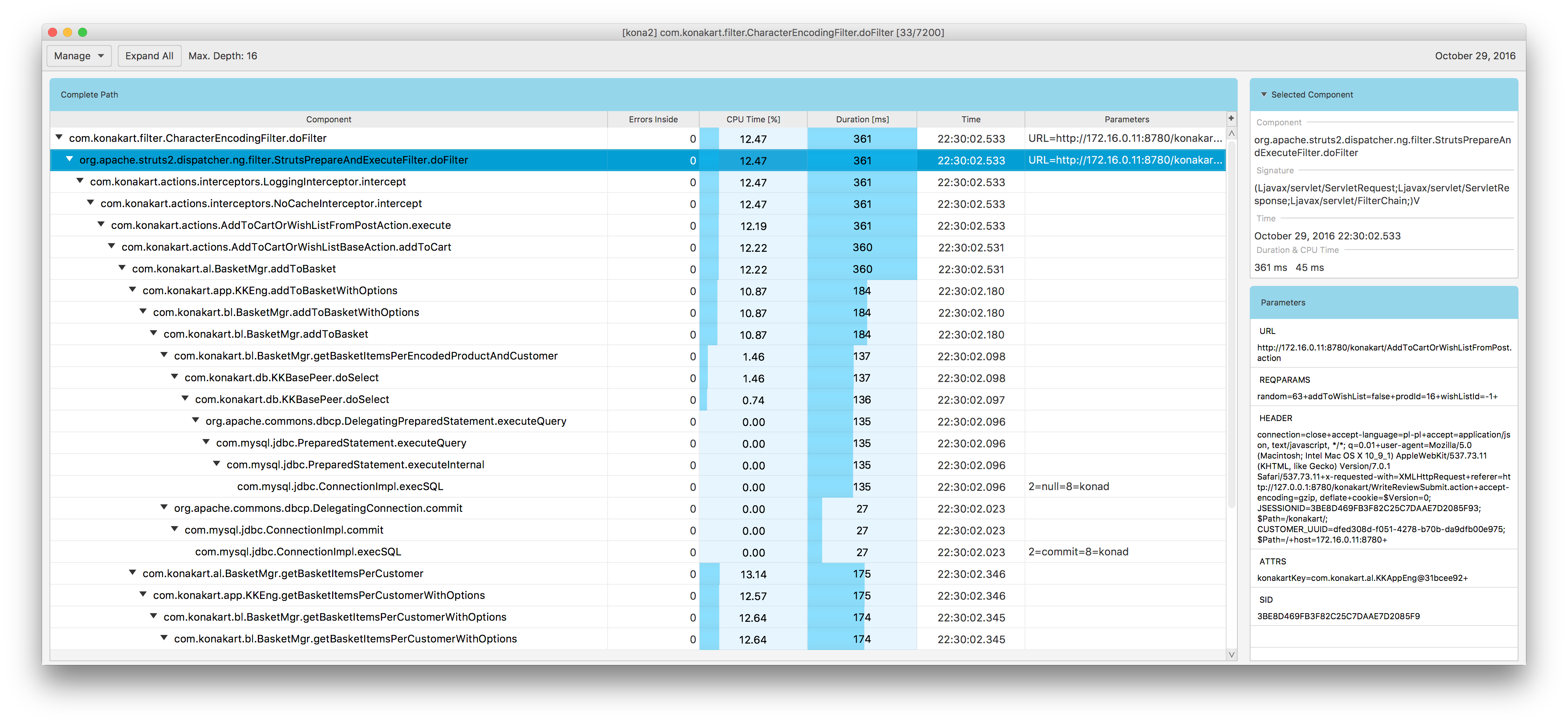
Fig. 1.35 Execution Stack
If you want to know the exact location of a method call within the execution stack, you can select the Manage –> Elements Position Visible on the stack details. Next time, you expand a branch on the execution stack you should see the positions of methods Fig. 1.36. The position is determined by two numbers, the first one denotes the sequence number within the stack and the second one denotes the stack depth.
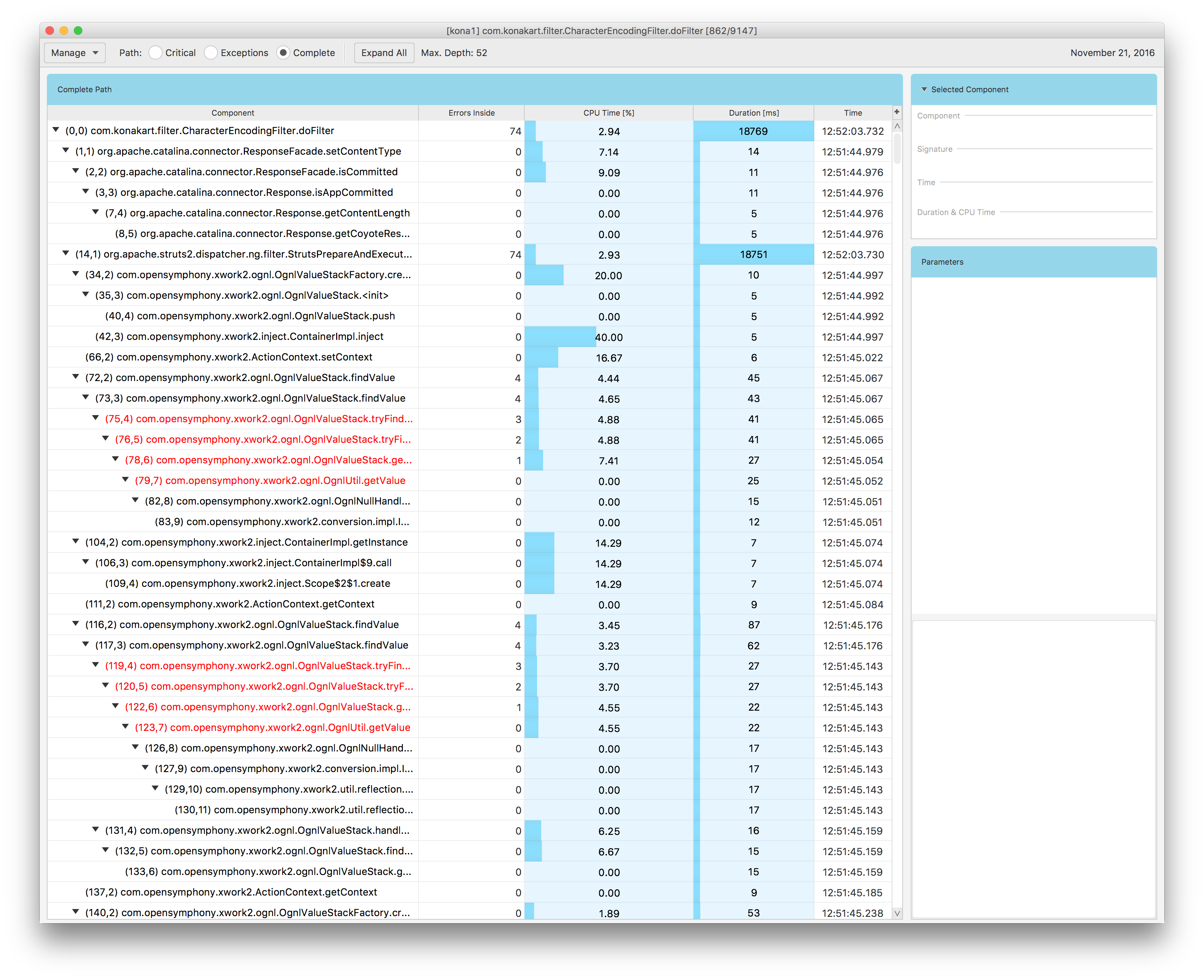
Fig. 1.36 Execution Stack: Methods Calls Position
When you click the Manage –> Switch View –> Table menu item, you will get a spectrum view Fig. 1.37. This view presents a spectrum of the execution stack, in other words it shows a collection of all the components which constitute the stack along with their calls and errors statistics.
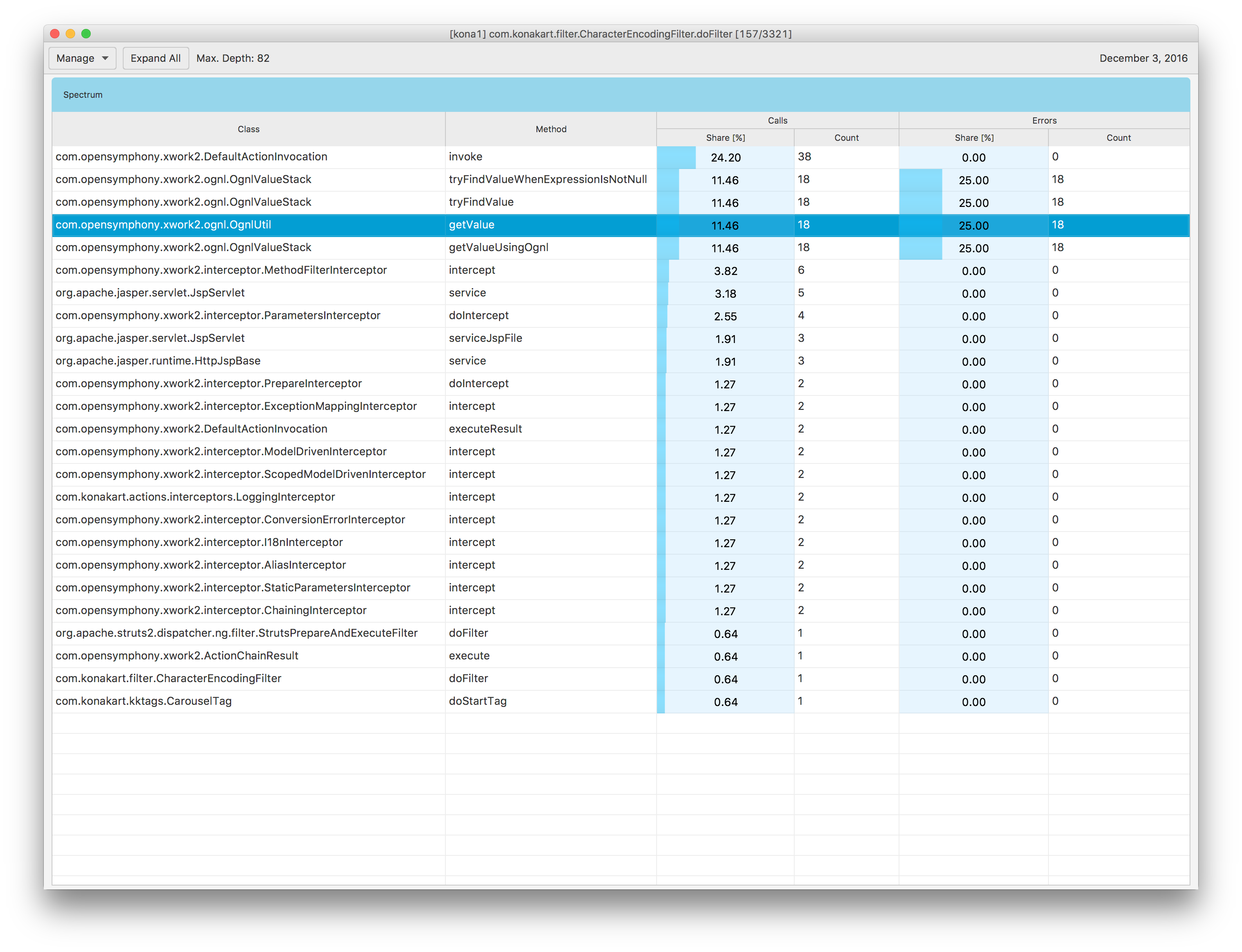
Fig. 1.37 Execution Stack: Spectrum
In Fig. 1.38 picture you can see four, sample execution stacks of some A method call. The first a view shows how the real execution stack looks. This is a real execution flow that takes place in your application. The second b view, presents the same stack instrumented by your agent. Depending on your configuration, the instrumentation may not cover the entire stack. The empty, gray boxes represent missed, uninstrumented methods. As you can see, at this very point your instrumented execution flow is not complete. Moreover, in your application runtime there can be situations when some of the instrumented method calls will not be reported (refer to Data Collecting Considerations for details). The empty, red boxes in the third c view represent this situation. Finally, what you actually observe in workstation is the last d view. This view presents an assembled stack with missing calls ignored. Now you know how to interpret the execution stack in workstation and why the resulting stack can differ from the original one.
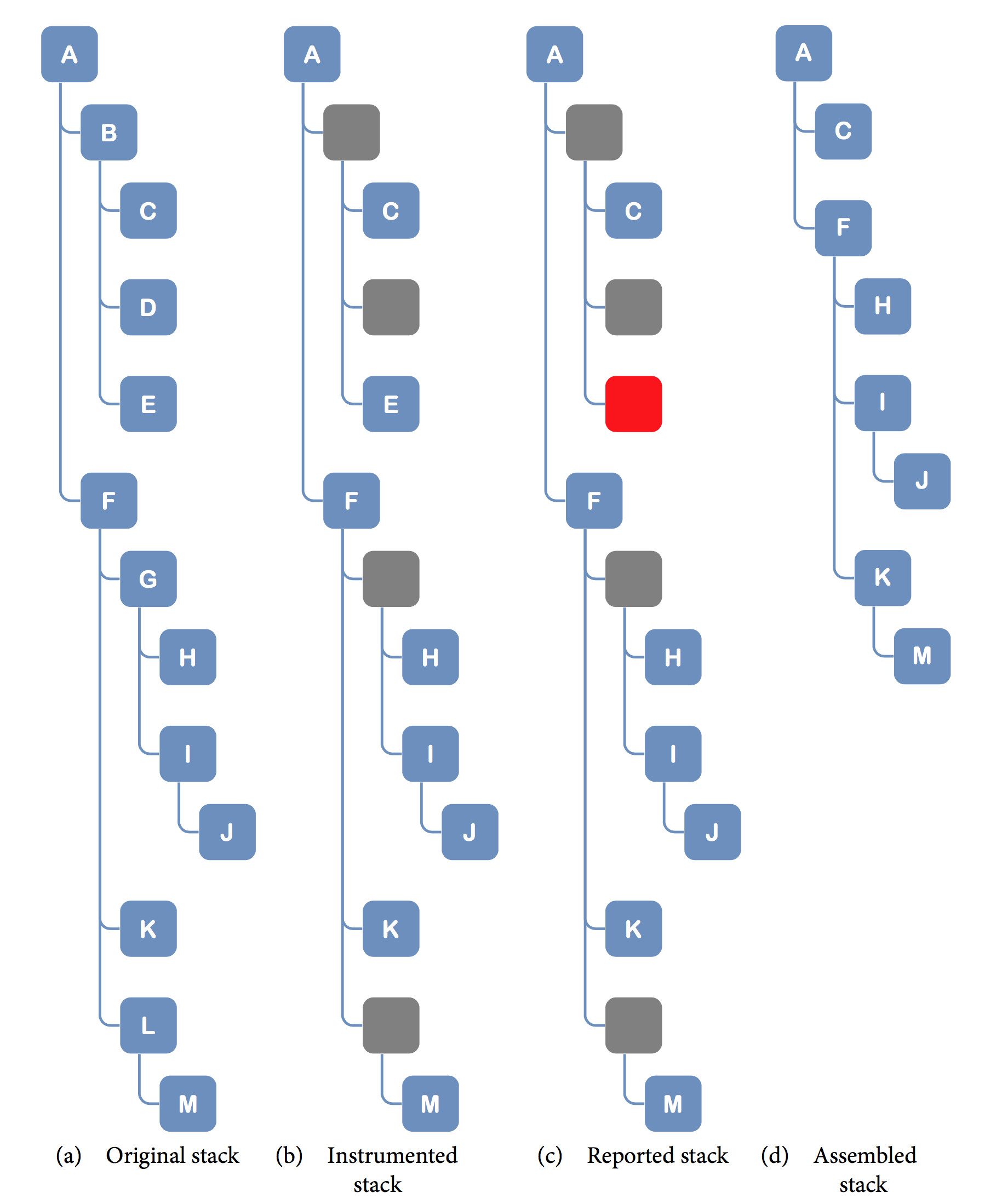
Fig. 1.38 Execution Stack Assembly
1.7.2. Flame Graph¶
When you click the Manage –> Switch View –> Flame Graph menu item on Fig. 1.35, you will get a Flame Graph view Fig. 1.39. This view presents an aggregated form of the execution stack. It is composed of frames (rectangles), which represent aggregated methods executions. The y-axis presents the stack depth. Although the x-axis itself has no meaning, the width of frames has one. There are three criteria, that change the way you define the frames width. These criteria can be selected exclusively on the top pane by clicking one of the radio buttons: CALLS, CPU and OFF-CPU. When the CALLS is selected, the frames width denotes how often a particular method was executed within the stack.
Note
Please, note there can be multiple frames representing the same method. This situation happens when a method is called in multiple places (on different execution levels) within the stack.
When the CPU is selected, the frames width shows how long methods spend on the CPU executing their code. Finally, when the OFF-CPU is selected, the frames width shows how long methods spend off the CPU.
The right side view of Fig. 1.39 presents a distribution of calls in the flame graph. Only top 20 calls are displayed for both CPU and OFF-CPU sets. By right-clicking on a selected record, you get a single menu item Find on Flame Graph from the context menu. When you click the menu item, each corresponding frame will be highlighted. In this way you can easily find where your method is located in the Flame Graph.
Note
The Flame Graph visualizations were introduced by Brendan Gregg. For more details about flame graphs please refer to http://www.brendangregg.com/flamegraphs.html.
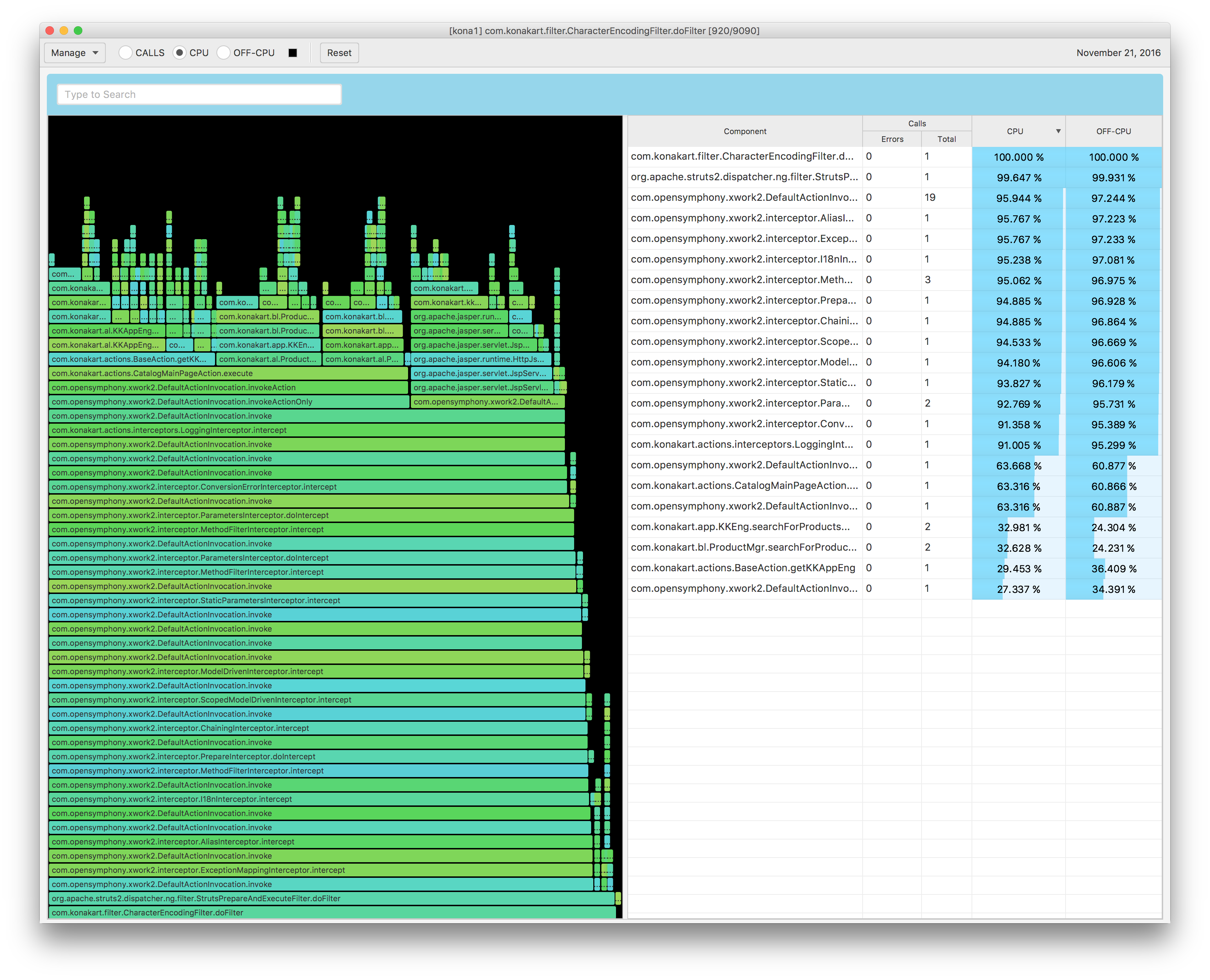
Fig. 1.39 Execution Stack: Flame Graph
1.7.3. Threads Subview¶
If you want to classify your query results by threads, just click the threads button in Fig. 1.34 and you will get a view similar to Fig. 1.40.
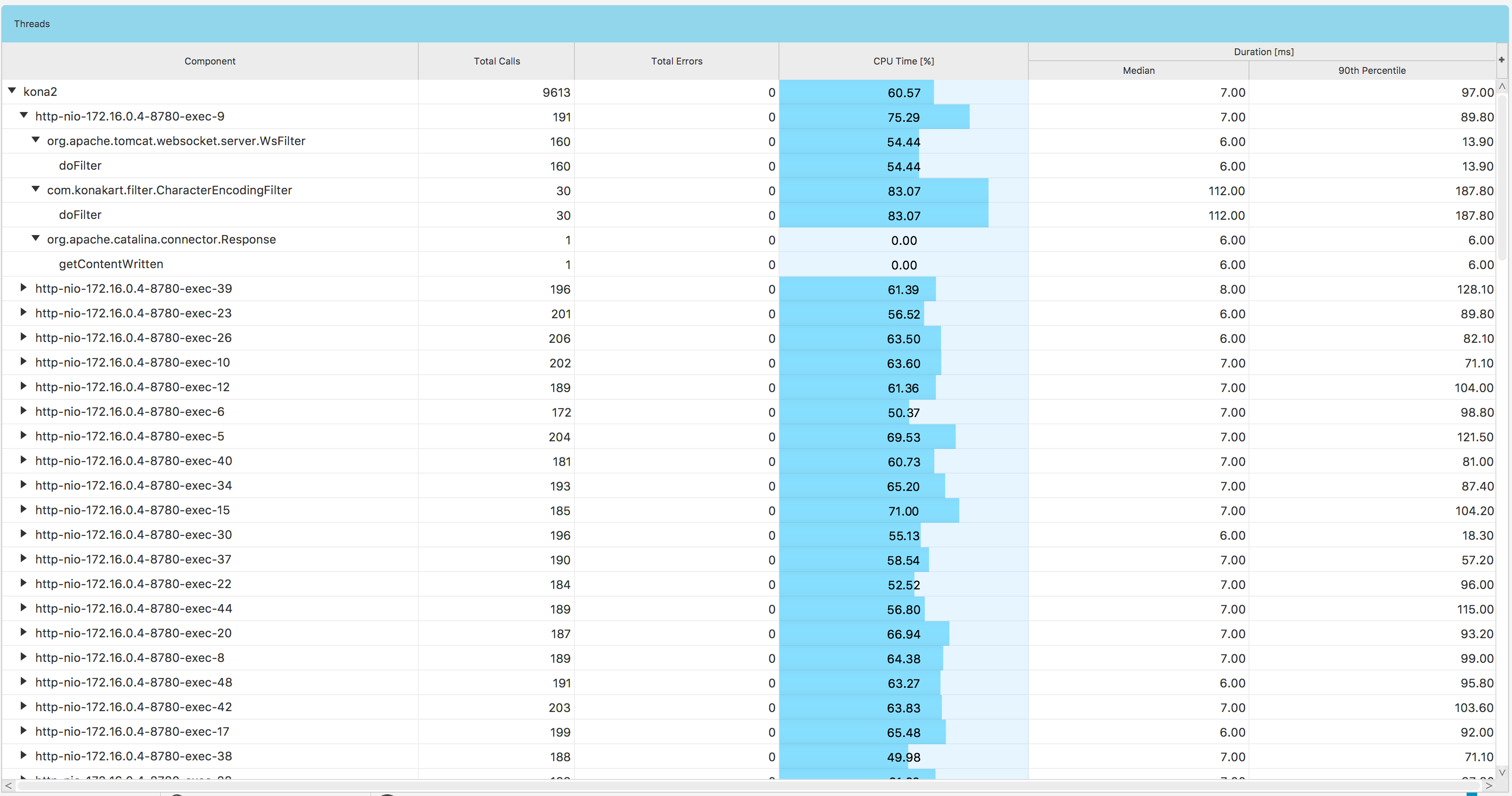
Fig. 1.40 Data Explorer: Threads Subview
The view contains a treetable with the following columns:
| Component: | A tree item, structured as agent –> thread –> class –> method. There are four component levels so the values in each column correspond to the current level. |
|---|---|
| Total Calls: | A total number of calls. |
| Total Errors: | A total number of exceptions thrown. |
| CPU Time: | A total CPU time (if enabled). |
| Duration Median: | |
| A median of duration. | |
| Duration 90th Percentile: | |
| A 90th percentile of duration. | |
In the Fig. 1.40 we can see there are 9613 calls reported by kona2 agent, where 191 calls were executed within http-nio-172.16.0.4-8780-exec-9 thread, 160 calls within org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsFilter class and 160 doFilter method executions.
1.7.4. Components Subview¶
When you can click the components button in Fig. 1.34 you will get Fig. 1.41 a view:
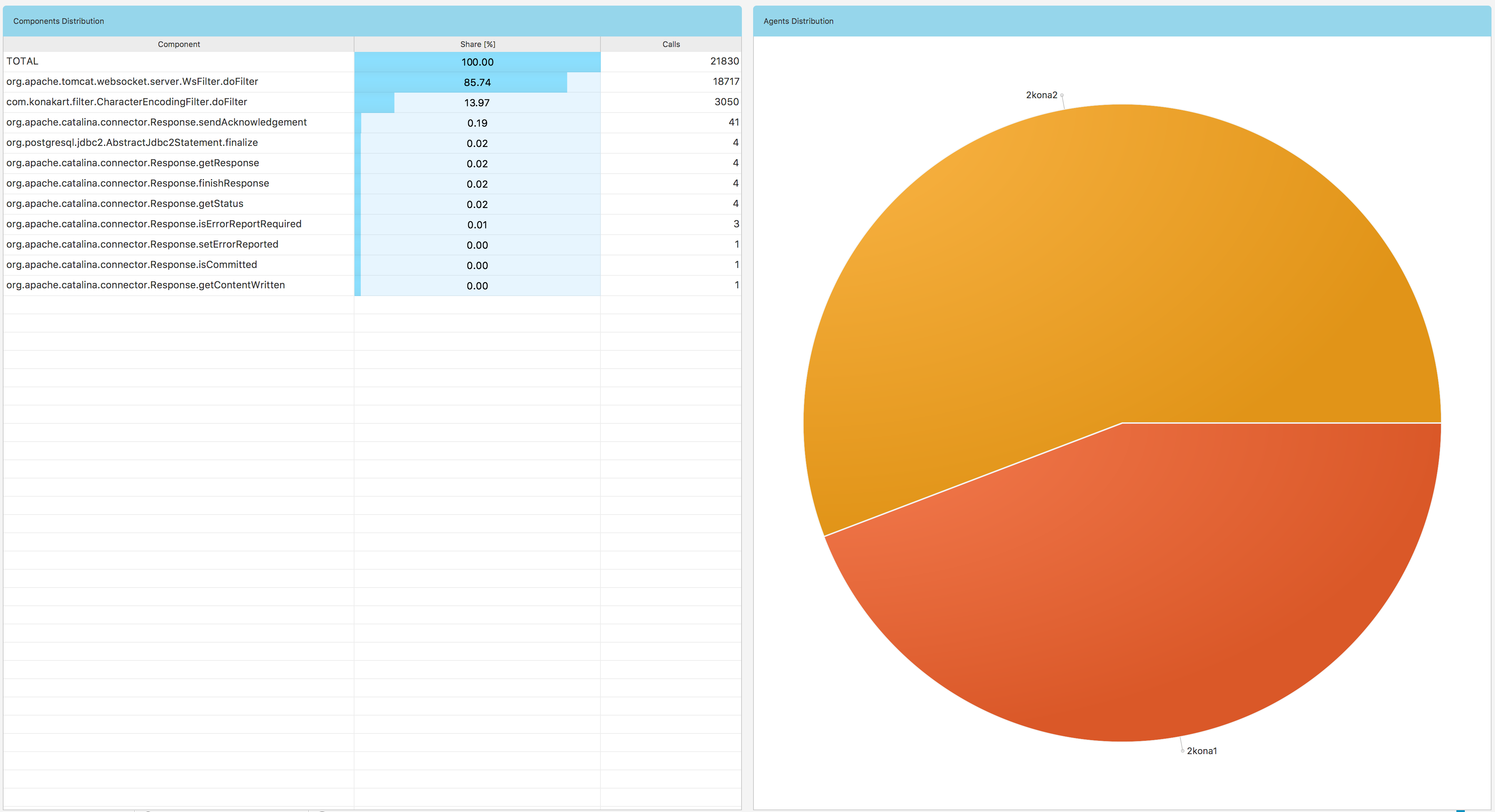
Fig. 1.41 Data Explorer: Components Subview
1.7.5. Errors Subview¶
When you can click the errors button in Fig. 1.34 you will get Fig. 1.42 view. In this view you can see what exceptions have been thrown and how their distribution looks like with respect to agents. When you click one of the exceptions you will get its distribution with respect to the agents.
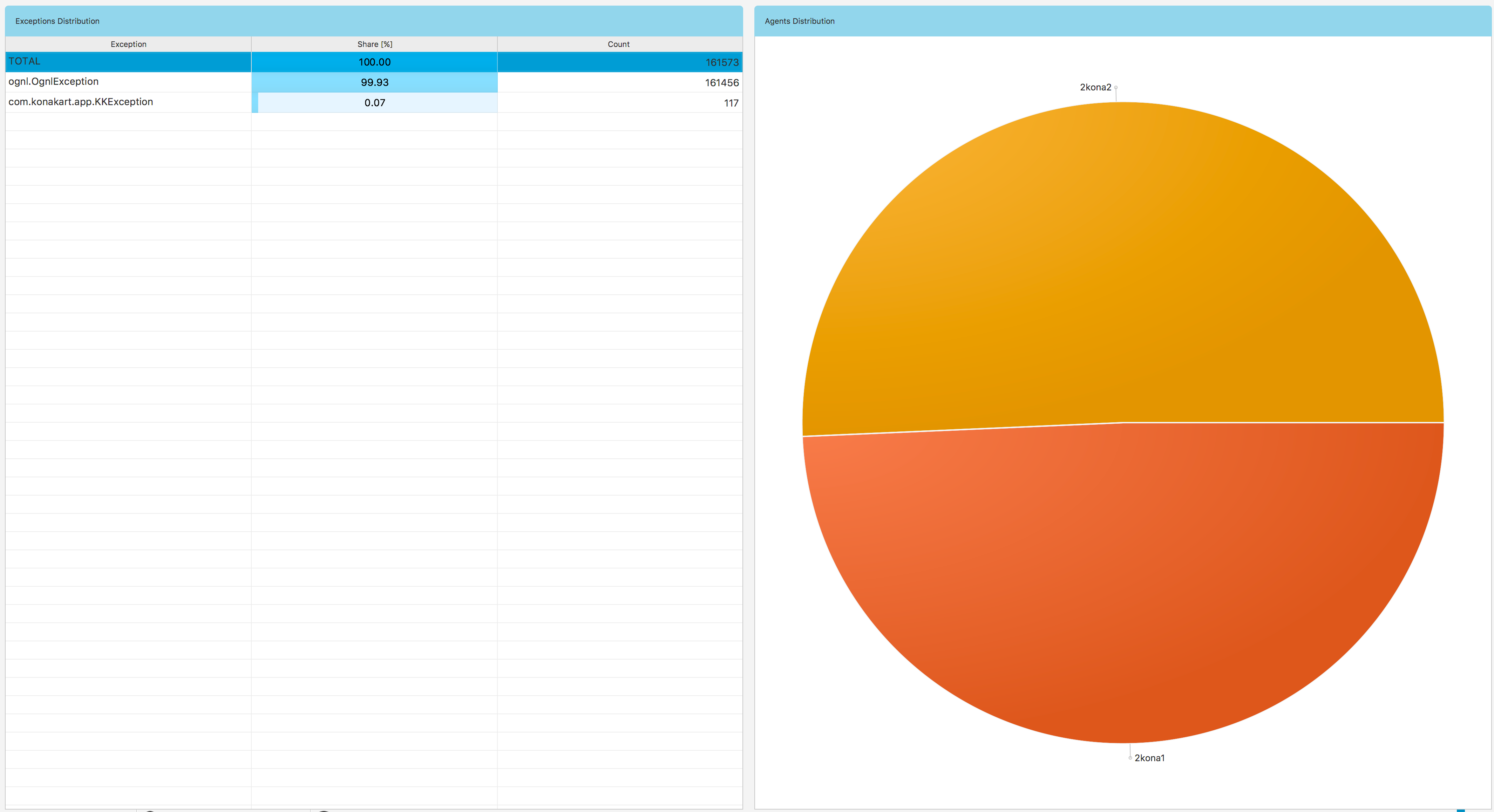
Fig. 1.42 Data Explorer: Errors Subview
1.7.6. Root Cause¶
If you click the root cause button in the summary pane ref{fig:fw:rcause}, you will get a Flame Graph generated from all the requests.
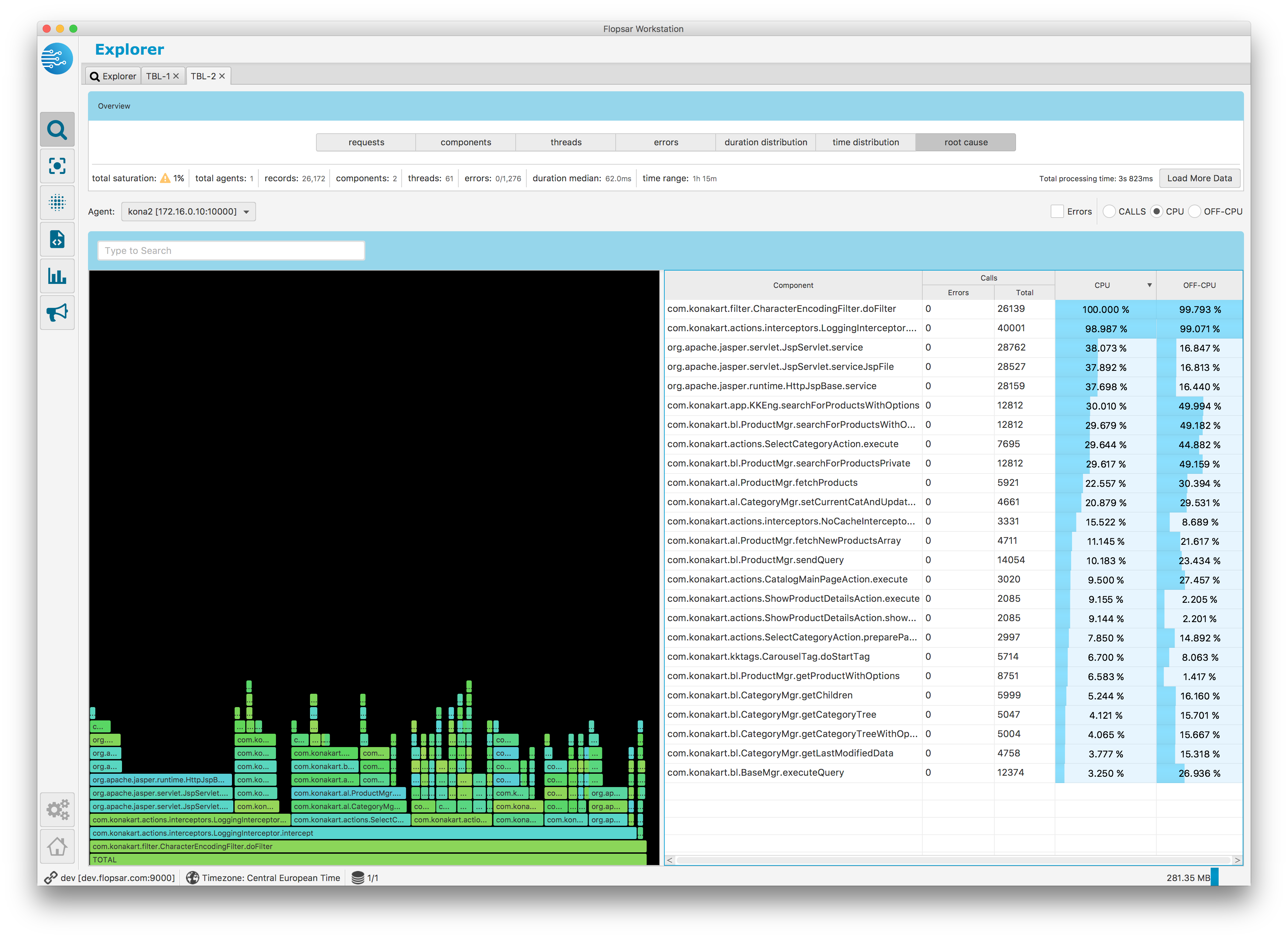
Fig. 1.43 Data Explorer: Root Cause
1.7.7. Time and Duration Subviews¶
If you click the duration median button in Fig. 1.34, you will get a bar chart Fig. 1.44 representing a distribution of calls duration. The bars colors correspond to agents.
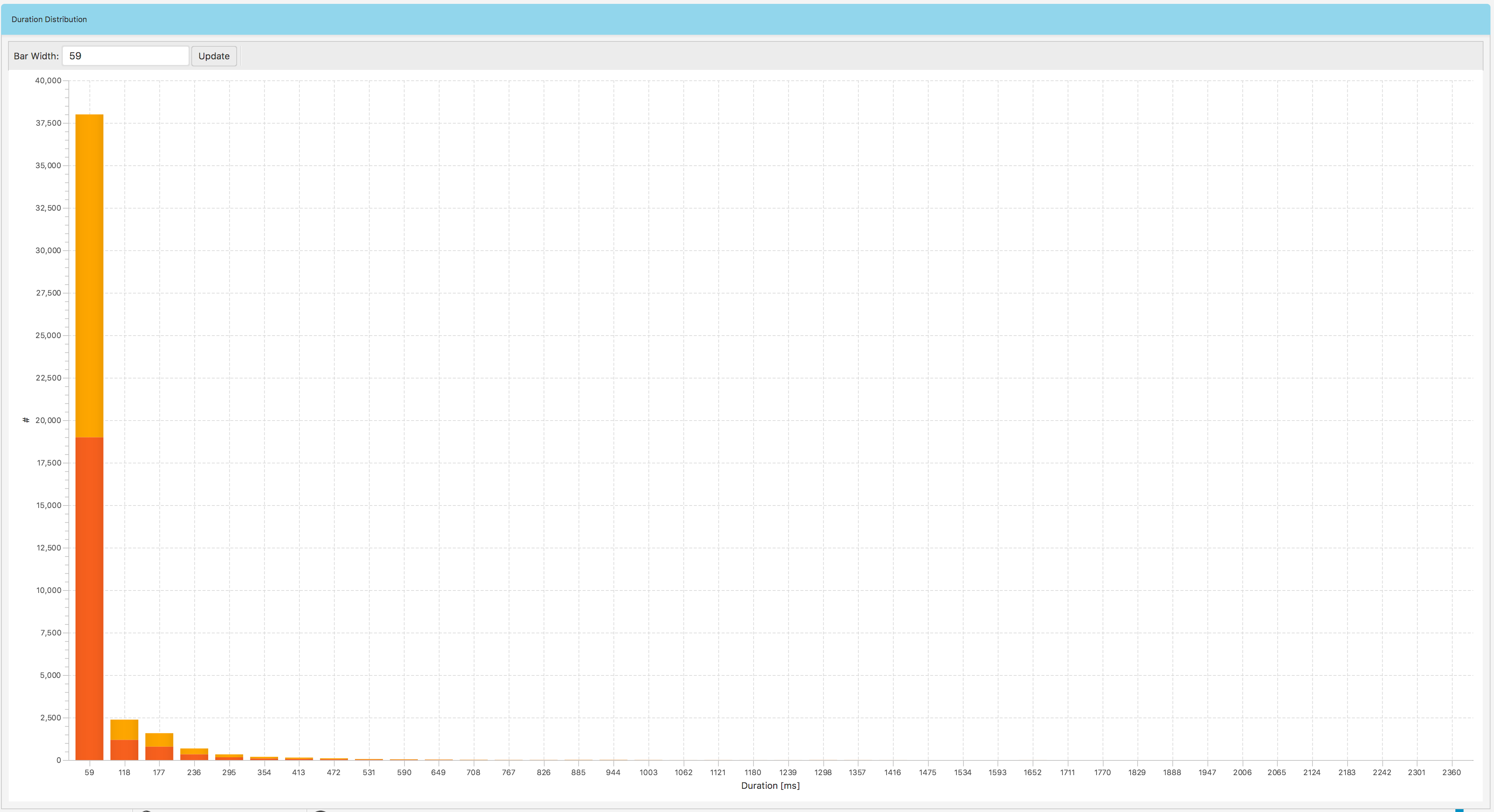
Fig. 1.44 Data Explorer: Duration Distribution
If you click the time range button in Fig. 1.34, you will get a bar chart Fig. 1.45 representing a distribution of calls count. The bars colors correspond to agents.
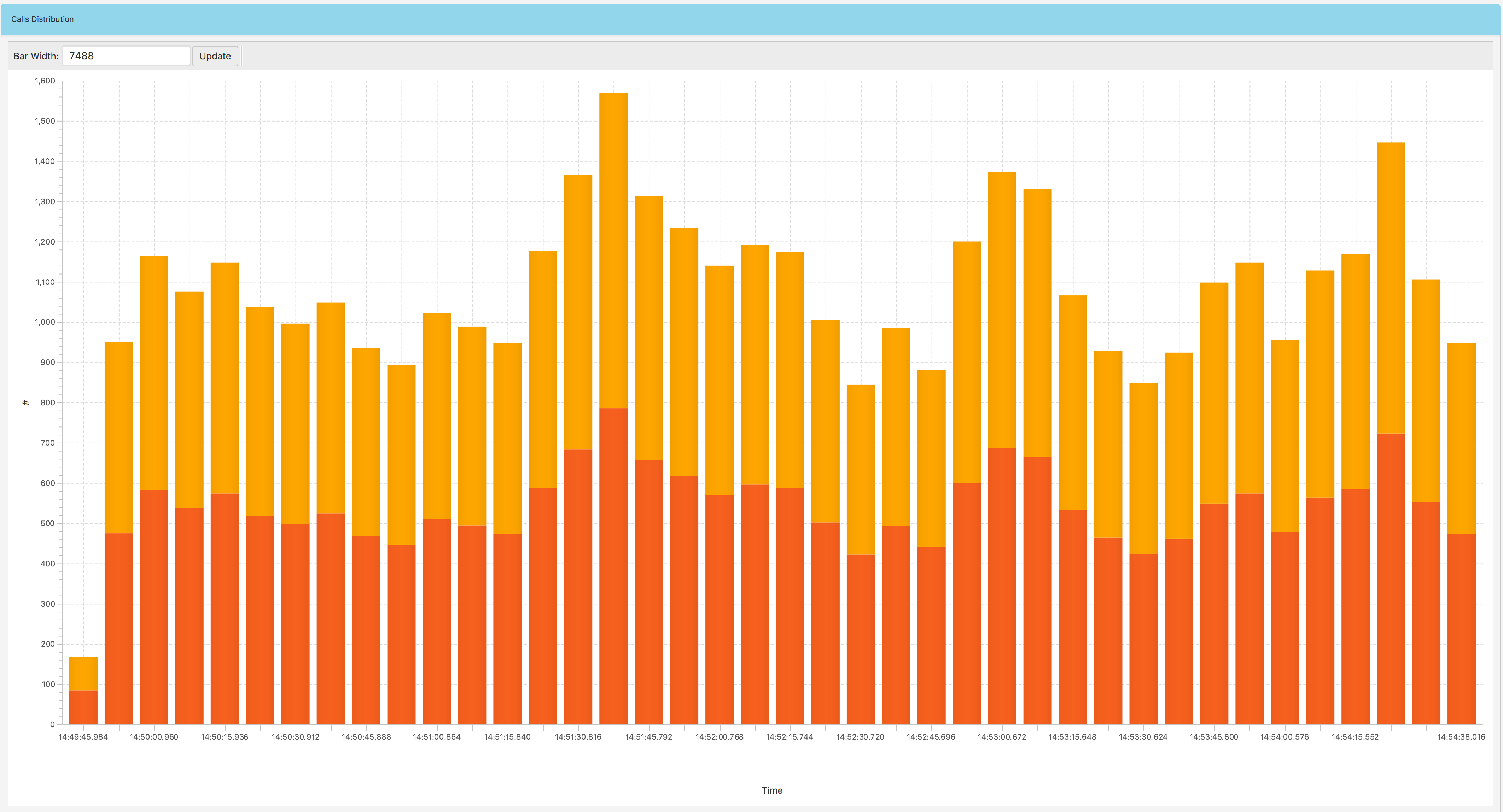
Fig. 1.45 Data Explorer: Calls Distribution
1.8. Exploring Environment Data¶
The environment data covers data of key-value type provided by either agent (JMX data) or another source of data, which uses agent API.
In order to explore the data you should toggle the Environment button (Fig. 1.33) to get the view Fig. 1.46. This view will allow you to retrieve data keys, which you can use later to draw some graphs. There are only two text input fields: AGENTS and METRICS. The first one is mandatory and you must specify a regular expression pattern for agent identifiers you want the data keys to be retrieved from. The second one is optional and you can specify a regular expression pattern for data keys you want to get.
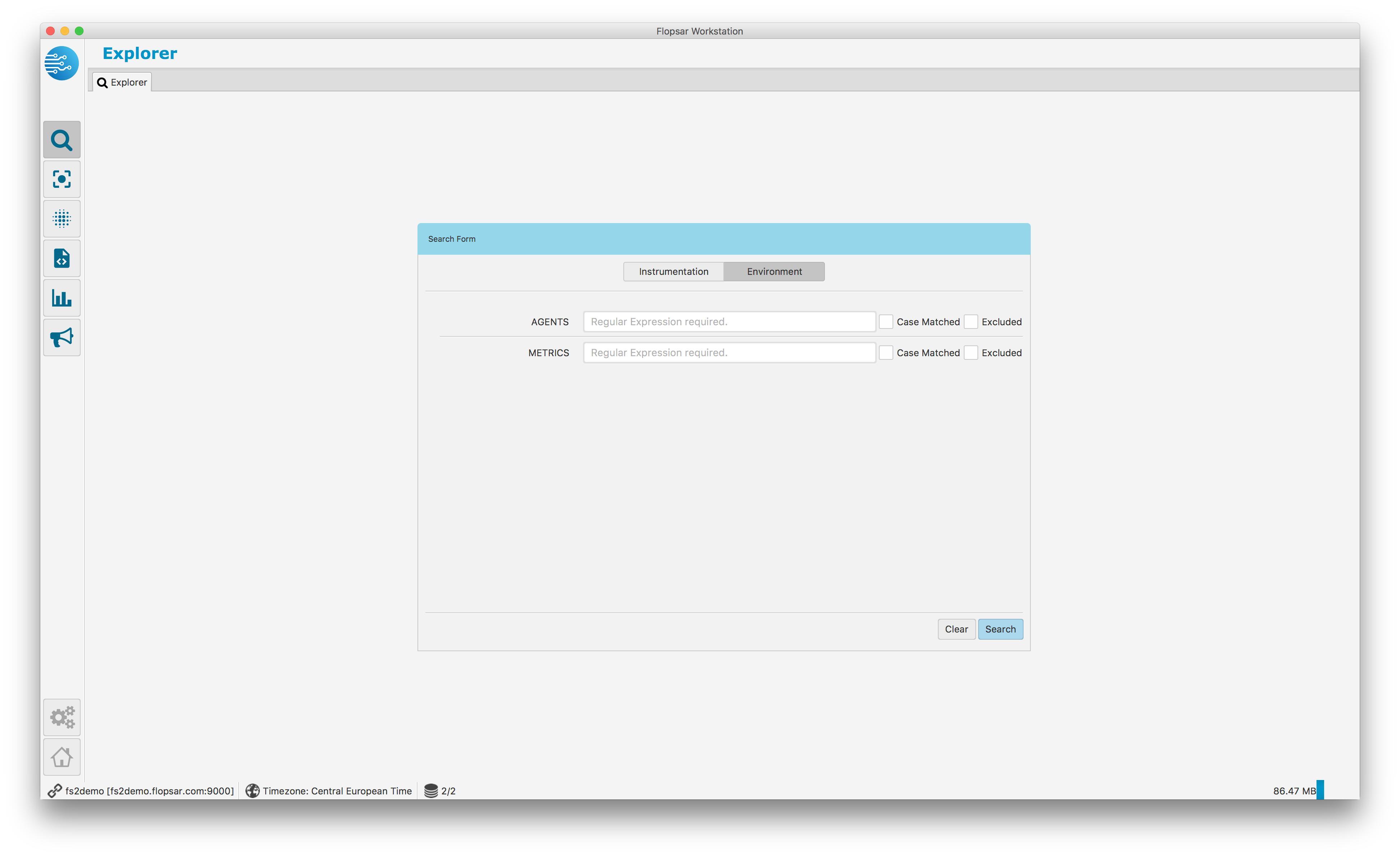
Fig. 1.46 Data Explorer: Environment Form
When you click the Search button, you will get the output similar to Fig. 1.47. The view contains a tree with all the found metrics keys. Each tree leaf has a context menu, which enables you to make a quick graph for the last 15, 30, 60 or 120 minutes. If you want to specify an exact time range for a graph, use the time range form at the top of the view. If you either use quick graph or time range form, you should get a graph on the right side of the view. Each time you make a graph, it is added to the graphs list on the right. If you want to remove a graph from the list, just click the cross icon in the top-right corner of the selected graph.
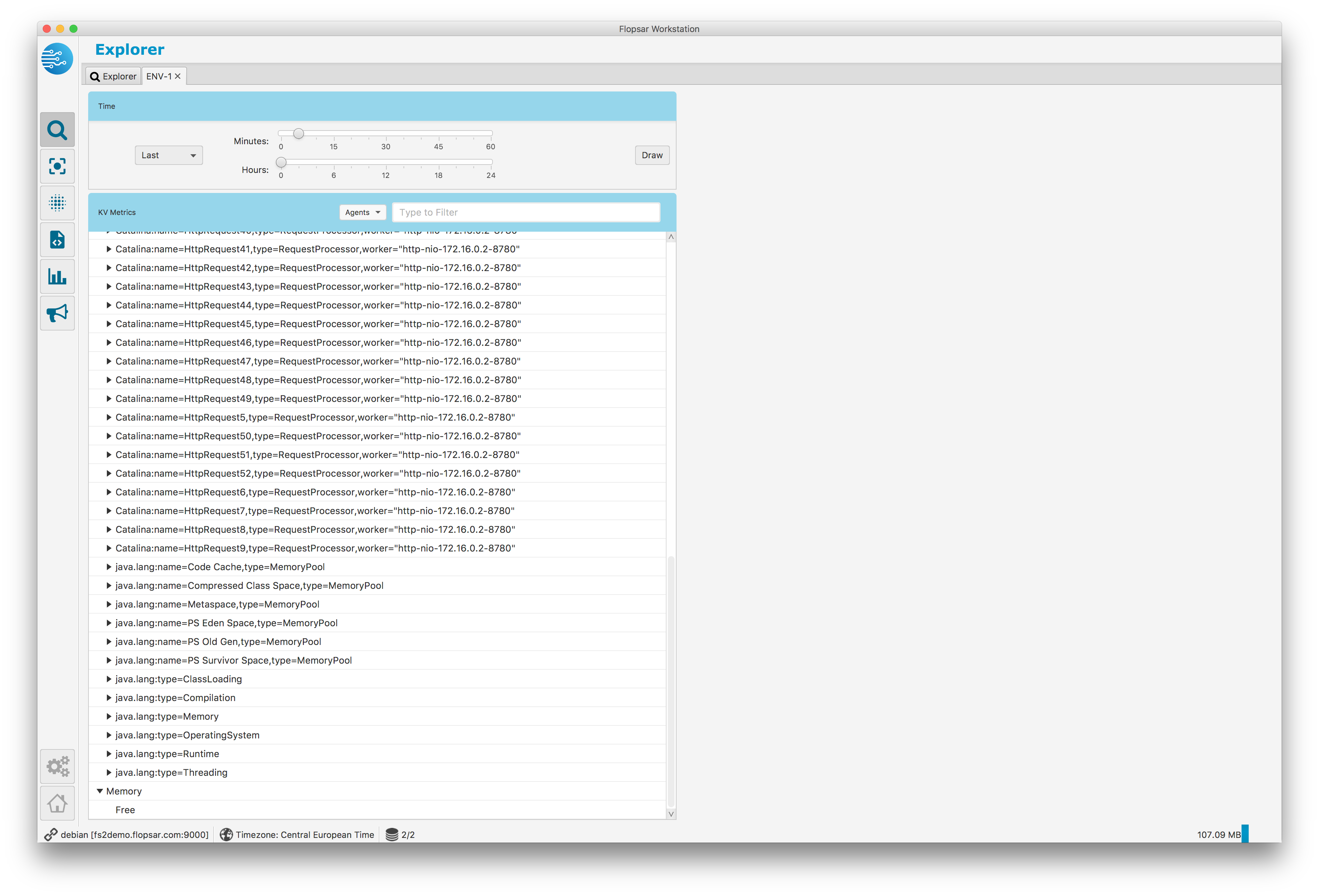
Fig. 1.47 Data Explorer: Environment Data Keys
When you click the Search button, the workstation sends a request to each database it is connected to and retrieves metrics for each agent, provided that the metric exists for the agent. As a result, there can be multiple graphs on a single graph pane and each graph corresponds to some agent. You can show or hide specific agents graphs by selecting the corresponding menu checkboxes in the Options menu. If you want to change graphs colors you can do it by clicking the Agents –> Colors menu item in the metrics keys list header.
The graphs vertical axis displays raw values, in other words the values that are collected by agents. No unit is displayed because workstation knows nothing about the data it retrieves. It can be any data, provided by either agent or some user customized agent. In case of JMX data, please refer to your application documentation to find out what units your JMX metrics use.
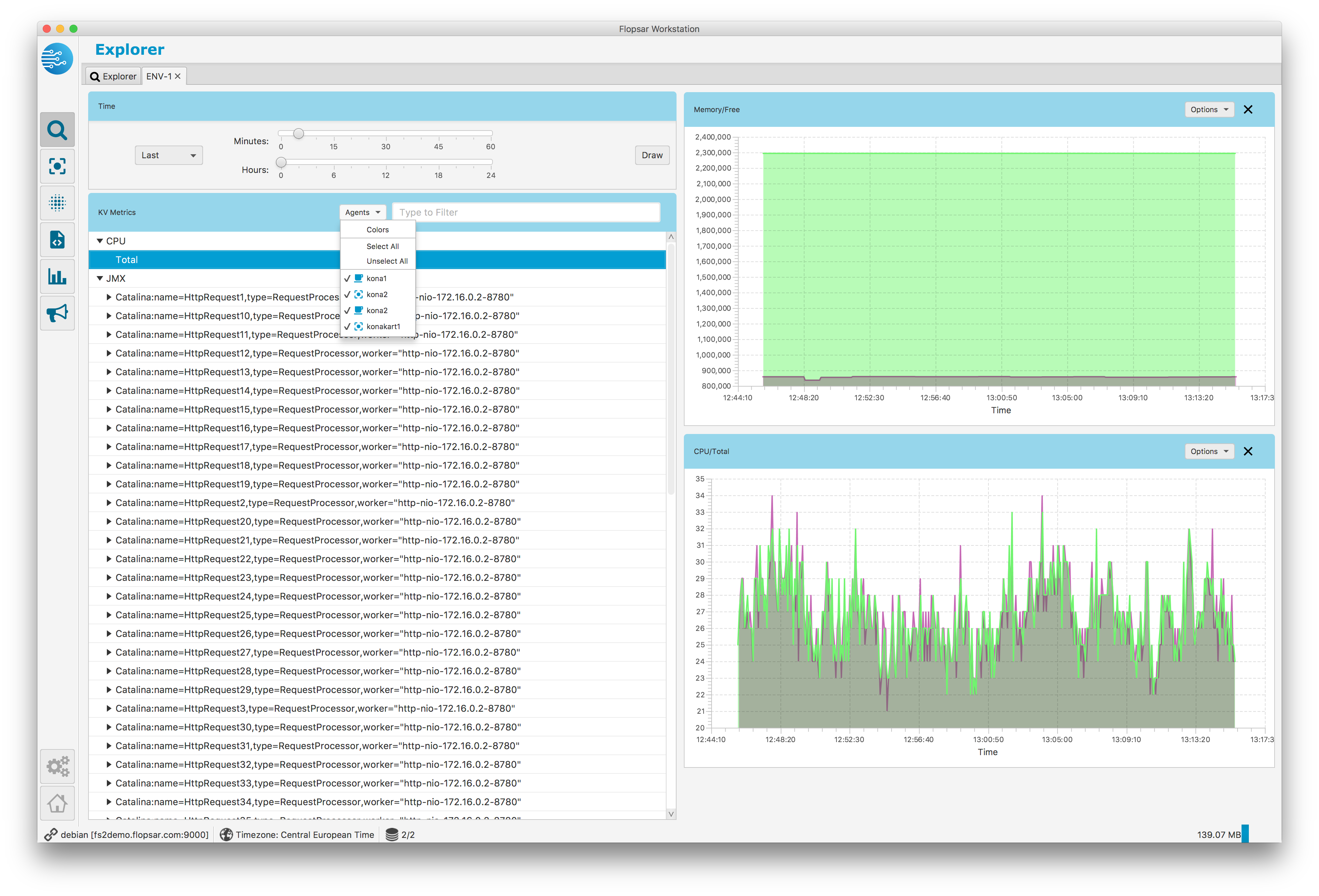
Fig. 1.48 Data Explorer: Environment Data Graphs
1.9. Monitoring Agents Health¶
Agents health can be viewed by clicking the Agents Health tile in the main view Fig. 1.3. If you click on some selected agent pane, you will see its status and health details.
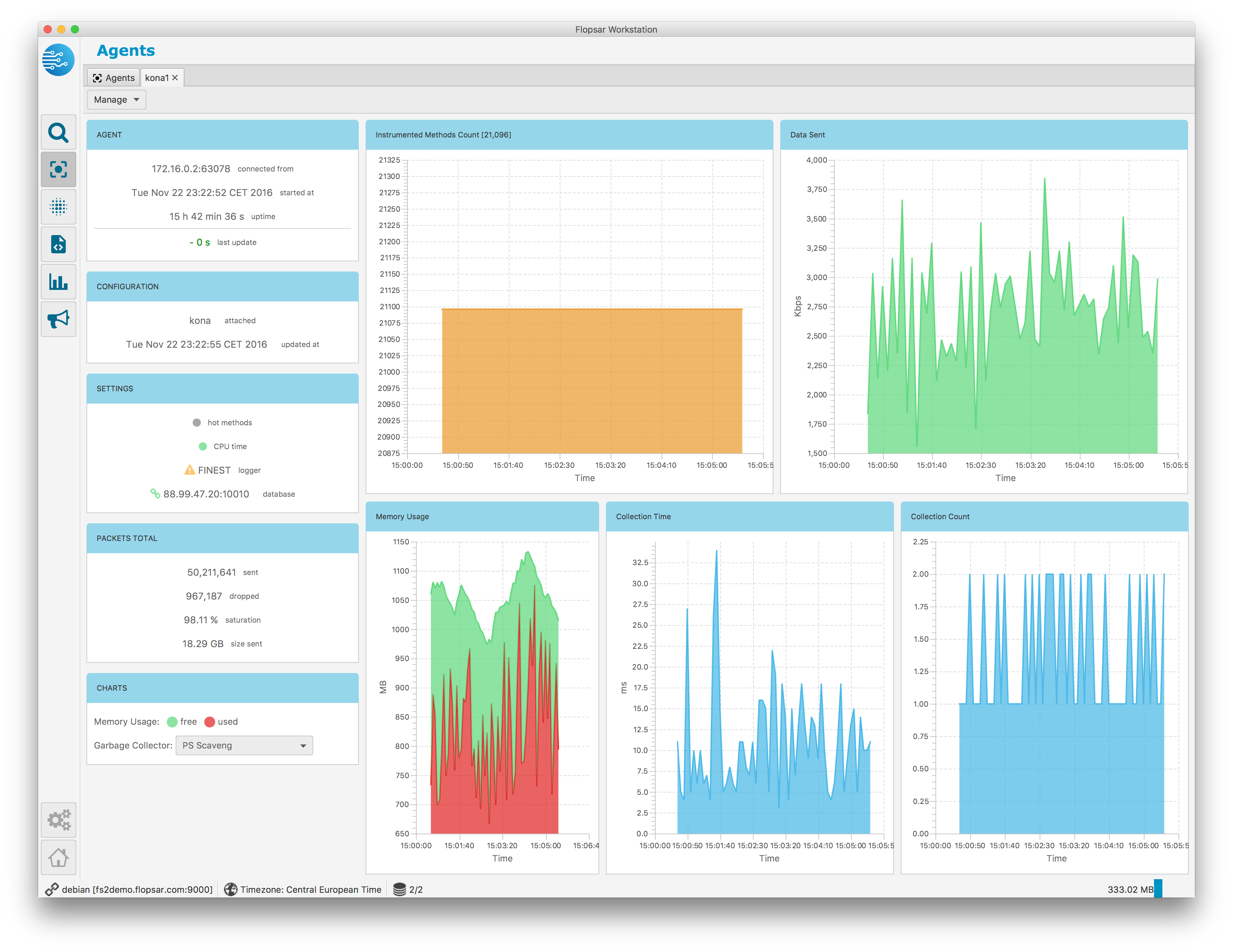
Fig. 1.49 Agent Status View
The view is divided into panes with either text information or graph on them. All the information in this view is reported by the agent.
The AGENT pane contains the following data:
| connected from: | Source socket address of the agent. It shows from which socket address the agent connects to manager. |
|---|---|
| started at: | Agent startup time. It shows when the agent started. |
| uptime: | Agent uptime time. It shows how long the agent is up. |
| last update: | Agent last report time. It shows how much time has passed since the last agent report received by workstation. When this time is greater than 15 seconds, it color turns from green to red. |
The CONFIGURATION pane contains the following data:
| attached: | Current configuration. It shows the configuration the agent is attached to. |
|---|---|
| updated at: | Agent configuration deployment time. It shows the last time a configuration has been deployed to the agent. |
The SETTINGS pane contains the following data:
| hot methods: | Hot Methods feature. It shows whether the Hot Methods feature is enabled or disabled. |
|---|---|
| CPU time: | CPU time feature. It shows whether the CPU time measurement is enabled or disabled. |
| logger: | Logger level. It shows the current logger level set. |
| database: | Current database. It shows the database the agent sends its data to. |
The PACKETS TOTAL pane contains the following data:
| sent: | Number of sent packets. Each method call, symbol or some metric value is represented as a single packet. These packets are sent to a database. This shows the total number of such packets sent to the database from the moment of the agent start. If the agent is attached to another database, this value will be reset. |
|---|---|
| dropped: | Number of dropped packets. It shows the number of packets that have been dropped inside the agents. There can be a few reasons which make the agent to drop packets. See ref{a-dc} for details. |
| saturation: | Packets saturation. It shows the ratio of the number of received packets to the total number of packets. This total number is a sum of dropped and received packets. The value is displayed in percentages. If the value is 100% it means that all the packets, that have been collected on the agent, have been received by the database. If this value is low, it means that a large number of packets is dropped for some reason. If the value drops below 50%, then a warning icon is displayed next to the value. |
| size sent: | Data size sent. It shows how much data has been sent to the database. This value is counted from the moment of the agent start. If the agent is attached to another database, this value will be reset. |
1.10. Managing Alerts¶
In order to make use of alerts features, you must ensure you have the notification plugin configured successfully (see Alerts for details). The alert feature enables you to set some rules that will trigger notifications whenever the rules conditions are satisfied. You can manage your rules in Fig. 1.50 view. The view contains a list of all rules and the settings pane of a currently selected rule.
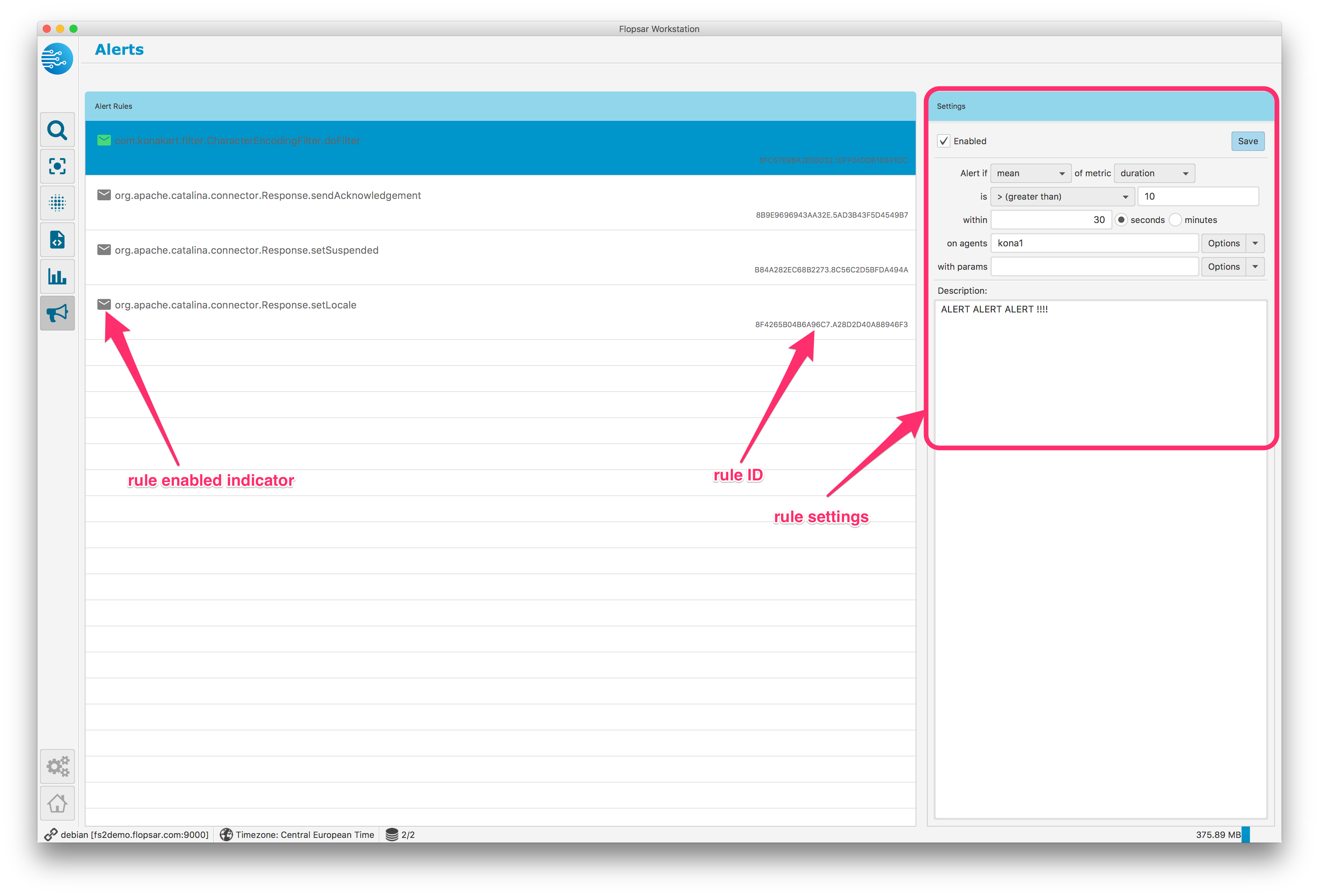
Fig. 1.50 Alerts View
The rules are persisted in manager and any changes made to them are global. Whenever you edit a rule and click the Save button, the rule is persisted in the manager and propagated to all the attached databases. Then the databases update their rules registry.
If you want to edit a rule, just select the rule by clicking the corresponding row of the list. You can either enable or disable the rule by selecting the Enabled checkbox. If the rule is enabled, the envelope icon on the corresponding row is green, otherwise is gray. You change the rule settings by updating the input controls on in the rule settings pane.
1.11. Analytics¶
Analytics is a special view Fig. 1.51, where you can collect and analyze method calls trends. The view is divided into three regions. The list on the left contains your analytics sets, the top region is a time range form and the central region is a list of a currently selected analytics set.
Fig. 1.51 Analytics View
1.11.1. Managing Analytics Sets¶
Whenever you add some entry to the analytics it must belong to one of analytics sets. Analytics sets are just logical groups that help you to classify your entries in the way you like. In order to add a new set, click the Manage –> Add New Set menu item and specify a label for this new set. All the analytics set are stored locally, on your machine you run the workstation on. If you want to use your sets on another machine, you must first export them and then import it on this new machine.
When you click on some analytics set, its entries are displayed in the list in the center. This list has a context menu, which enables you to either duplicate or delete the selected entries. If you want to edit the selected entry, just double-click on it. A popup window Fig. 1.52 should appear then. There are two text inputs where valid regular expressions are expected. The Agent text field is used to specify a pattern for agents’ names and the Parameter text field to specify a pattern for parameters. The Parameter input is optional and can be empty.
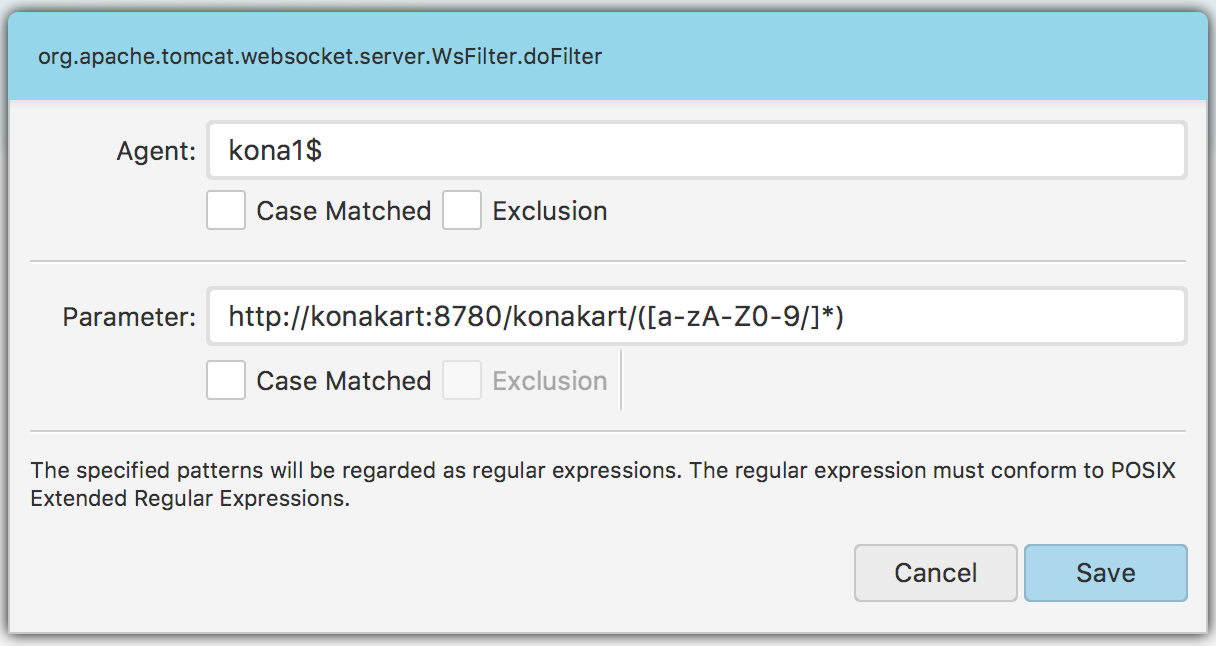
Fig. 1.52 Analytics Set Entry
Depending on the Parameter text field value you can obtain different results. If you do not use a subexpression, you will obtain the result similar to Fig. 1.54. If you use a subexpression, you will get the result similar to Fig. 1.53.
Note
Only a single subexpression in the Parameter text field is allowed.
In other words, if you want to obtain results grouped by some expression, you should put that expression pattern in parentheses so that it forms a subexpression.
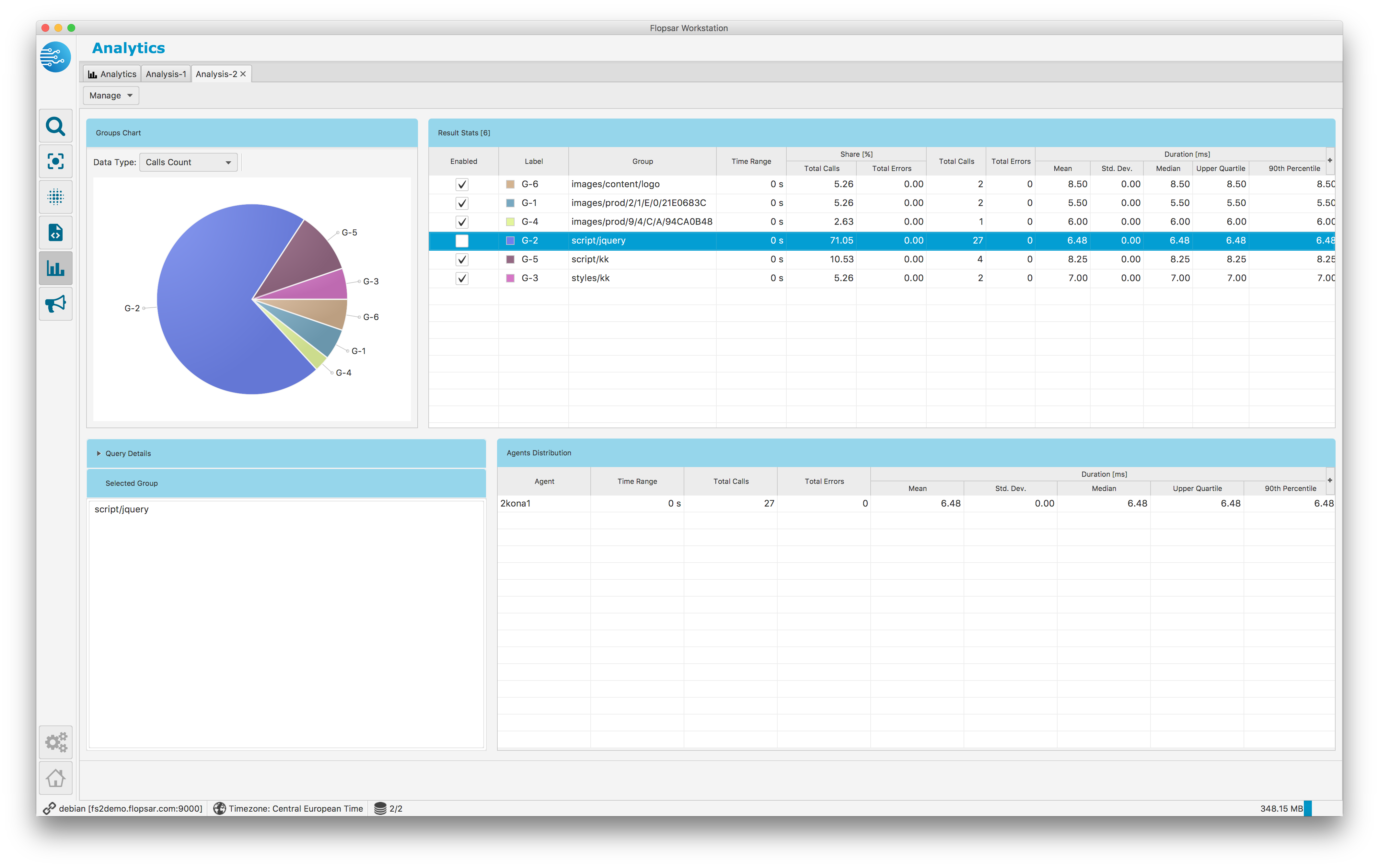
Fig. 1.53 Analytics Result: Group By
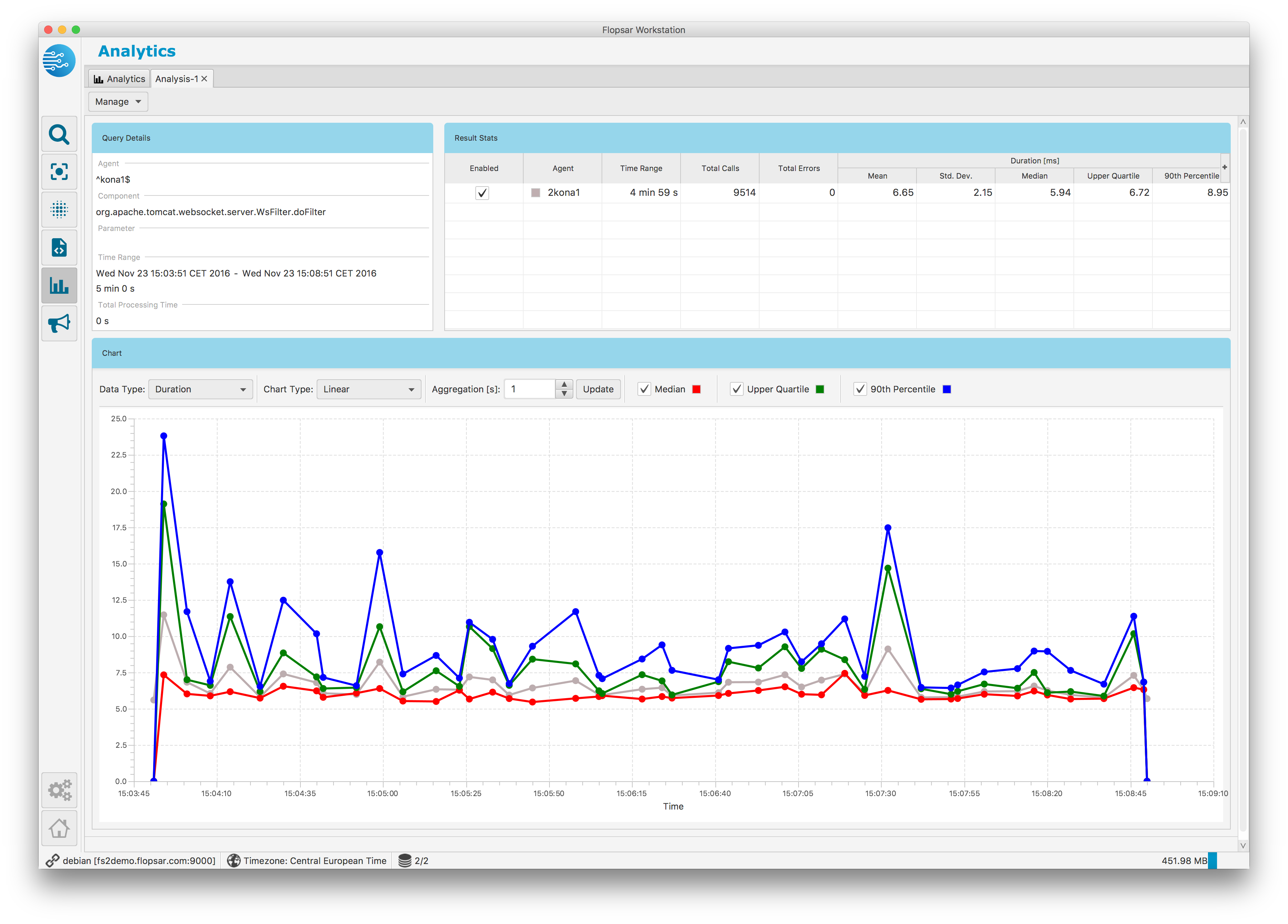
Fig. 1.54 Analytics Result: Duration Graph
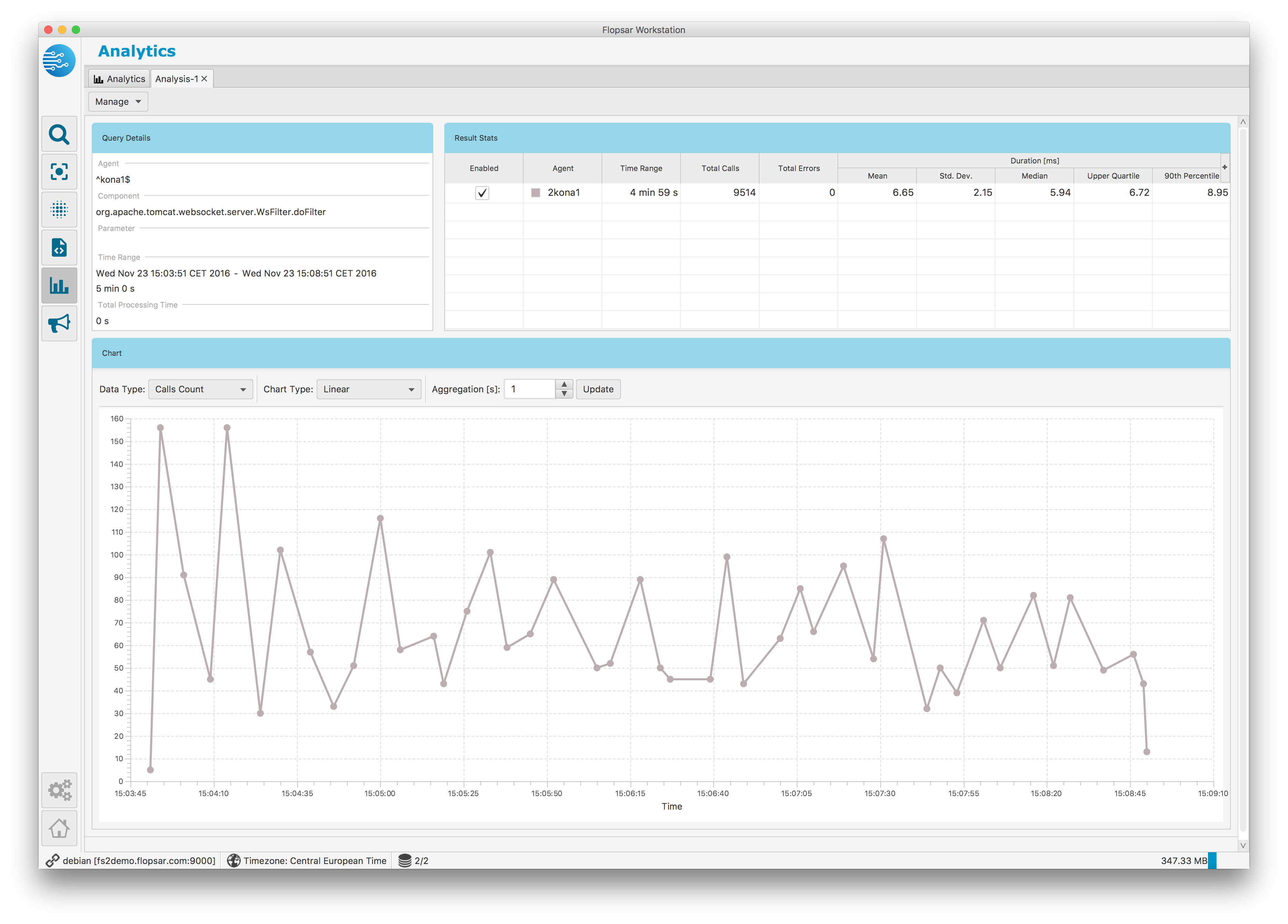
Fig. 1.55 Analytics Result: Calls Graph